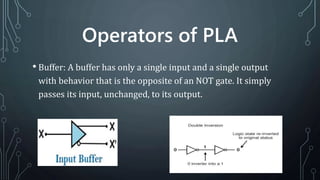
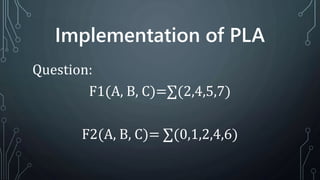
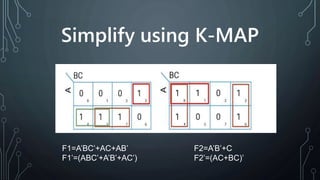
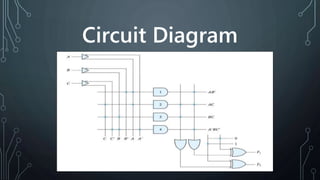
The document discusses programmable logic arrays (PLAs), which are a type of programmable logic device (PLD) that contains an array of AND gates and OR gates. A PLA allows both the AND array and OR array to be programmed. It can implement combinational logic functions through a sum of products. The document compares PALs, PROMs, and PLAs, and provides details on the components and operation of a PLA, including examples of implementing logic functions with a PLA using K-maps and a programmable truth table. Advantages and disadvantages as well as applications of PLAs are described.