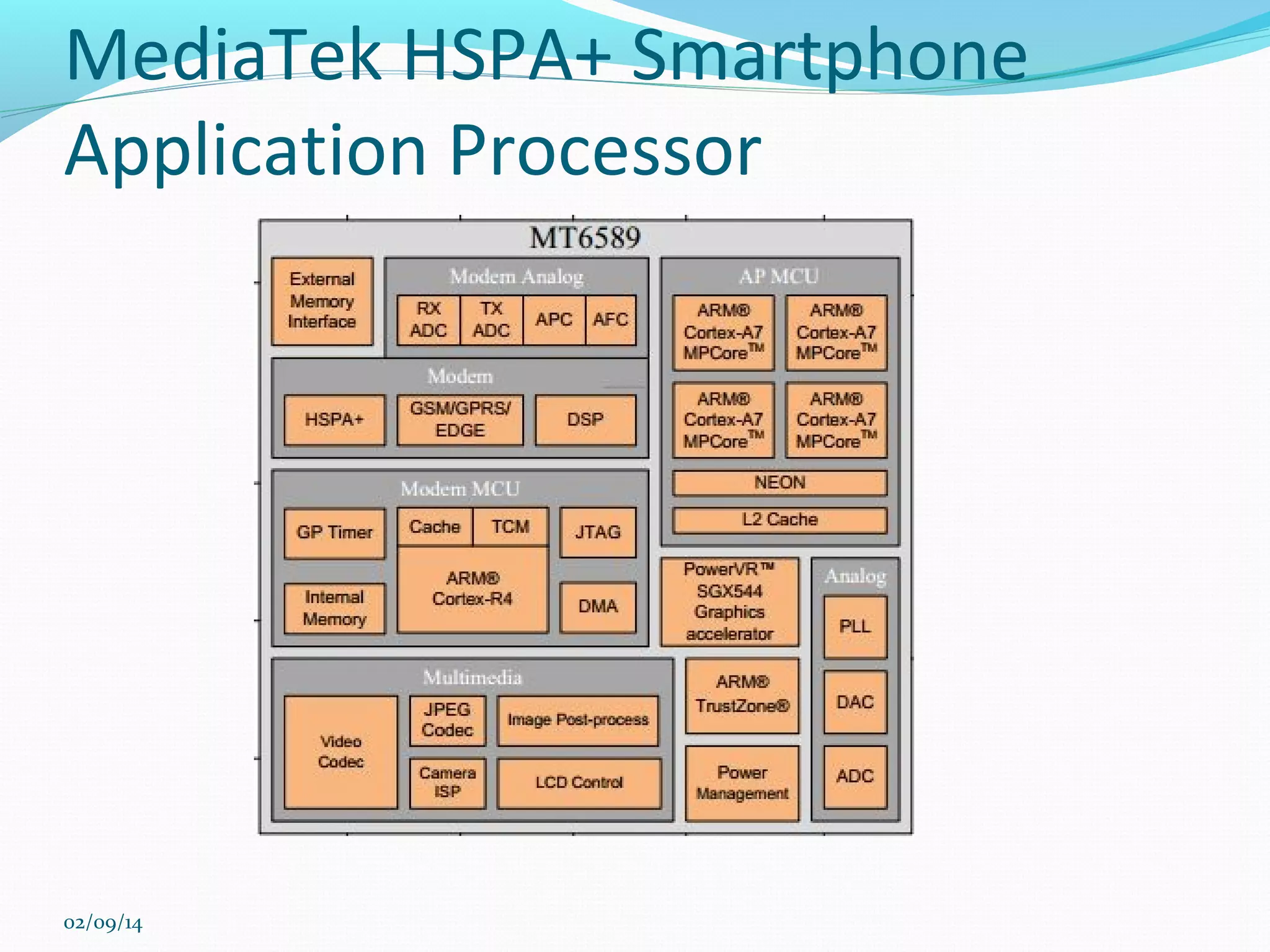
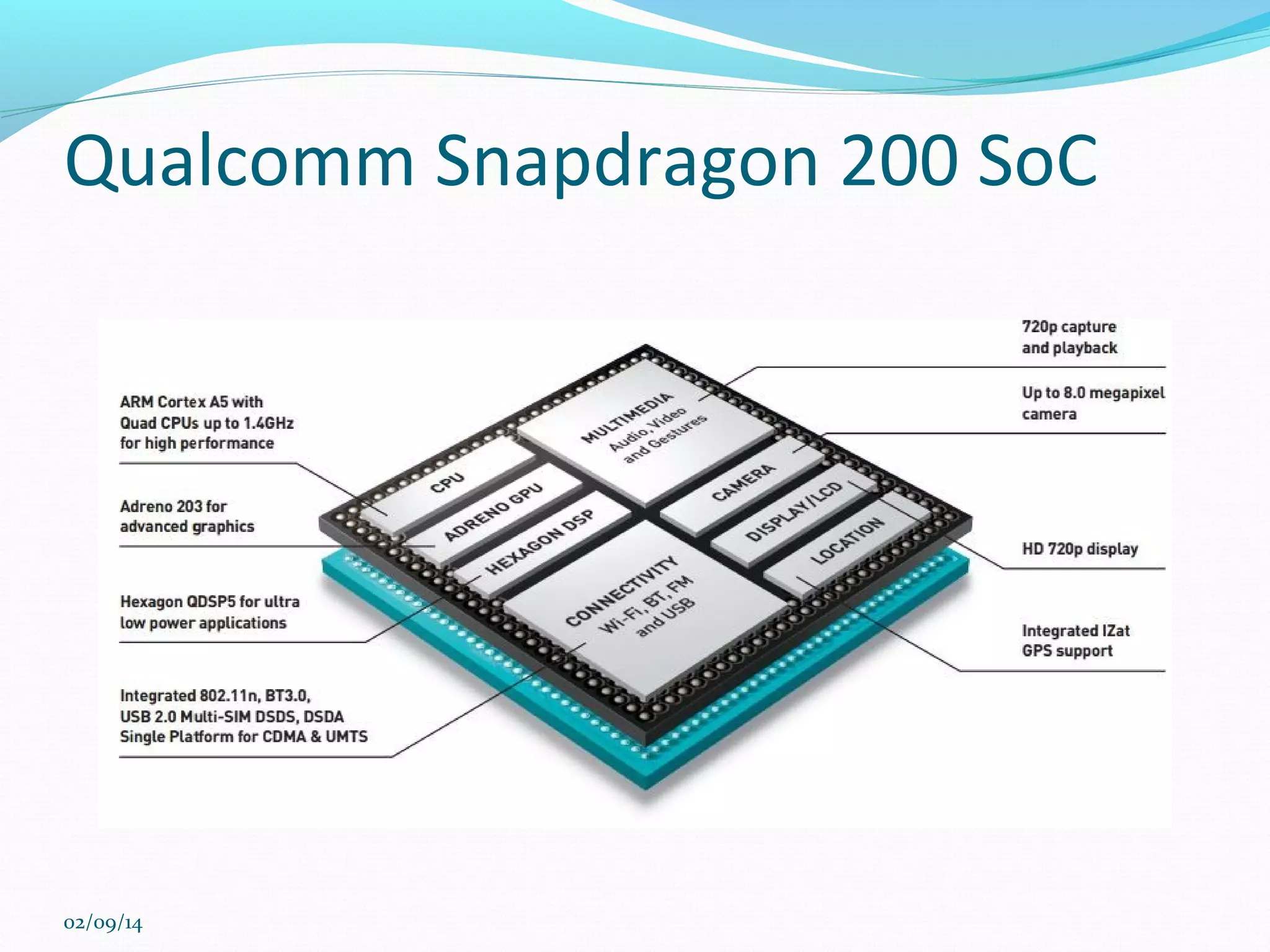
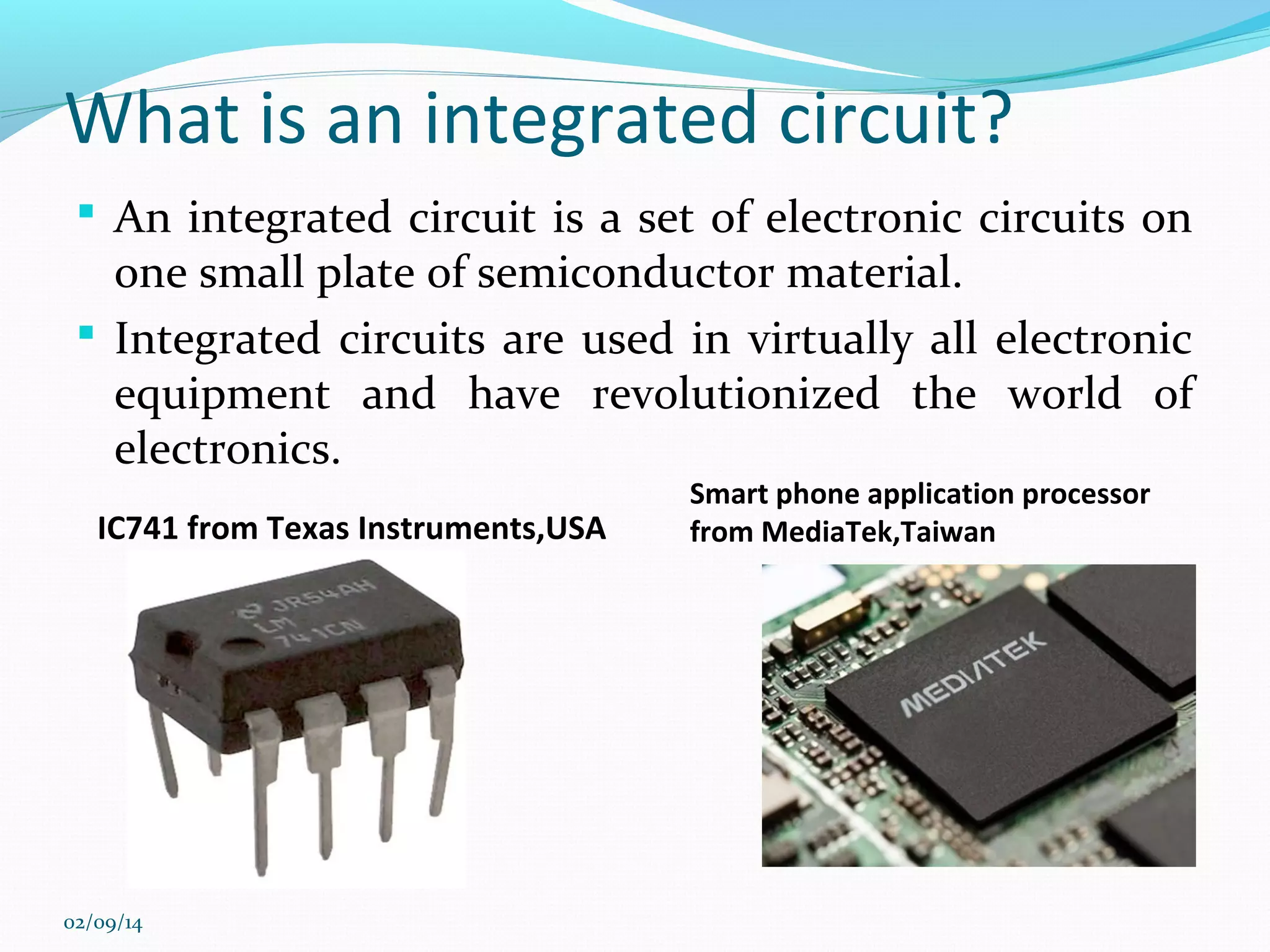
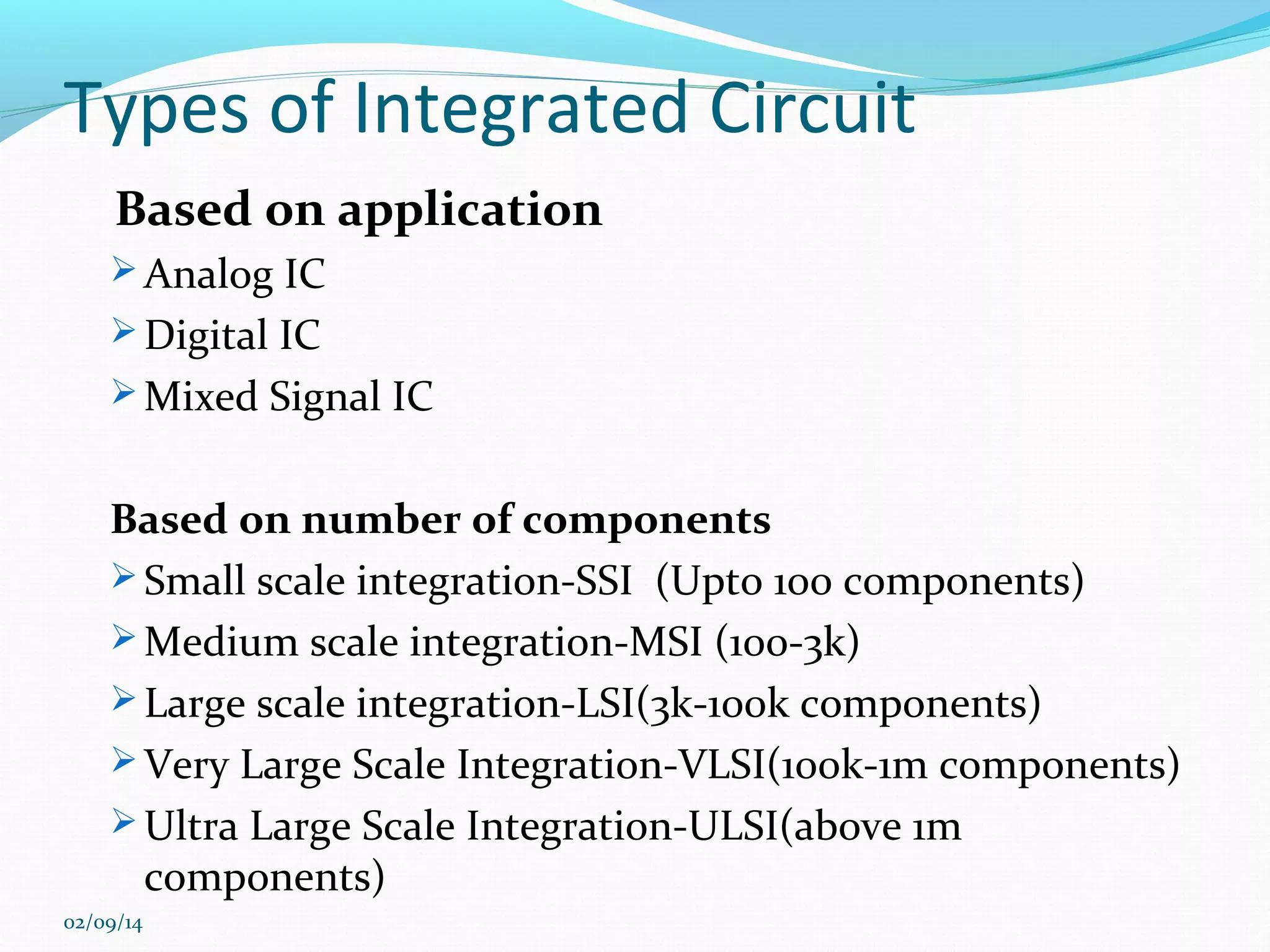
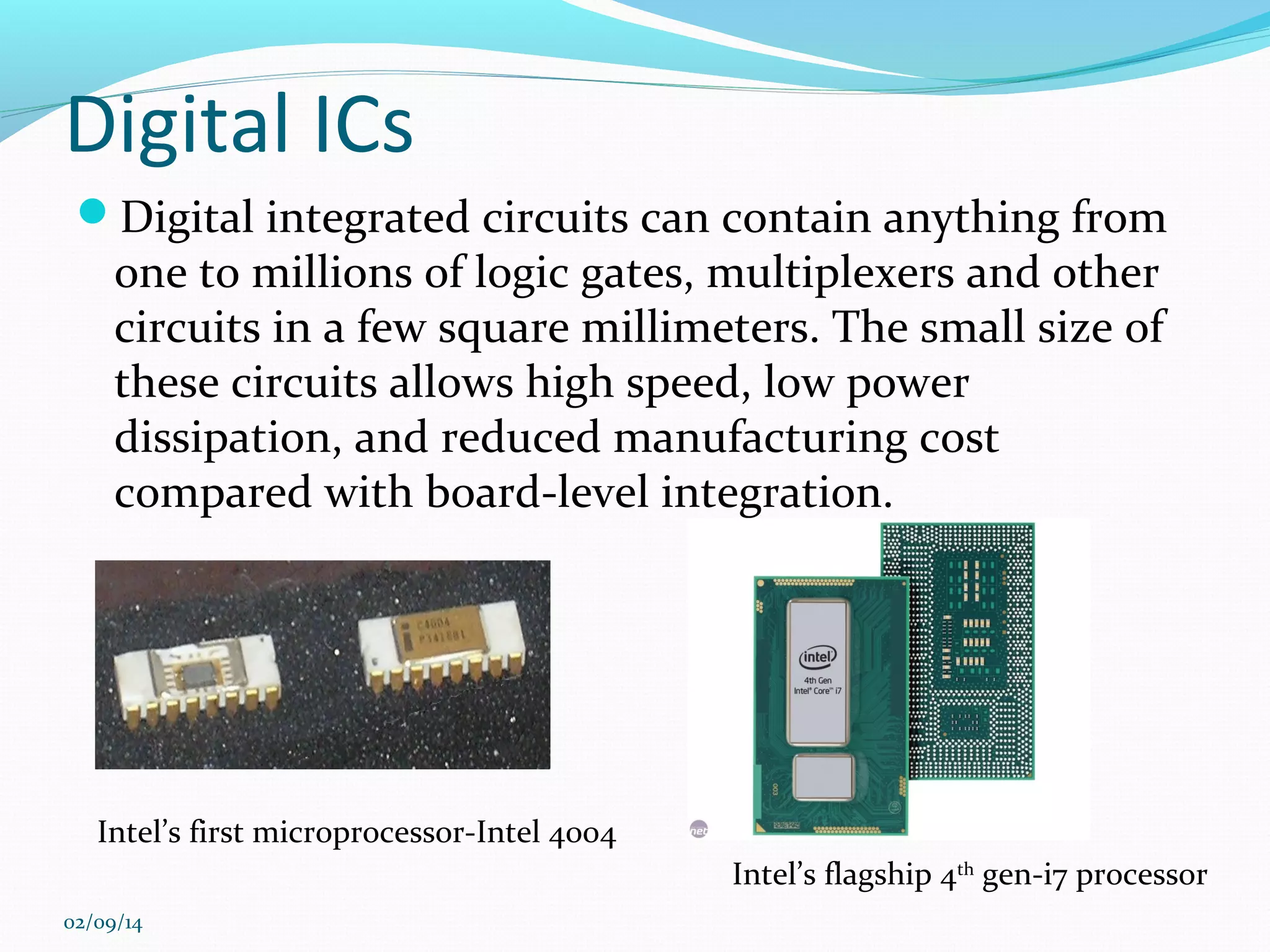
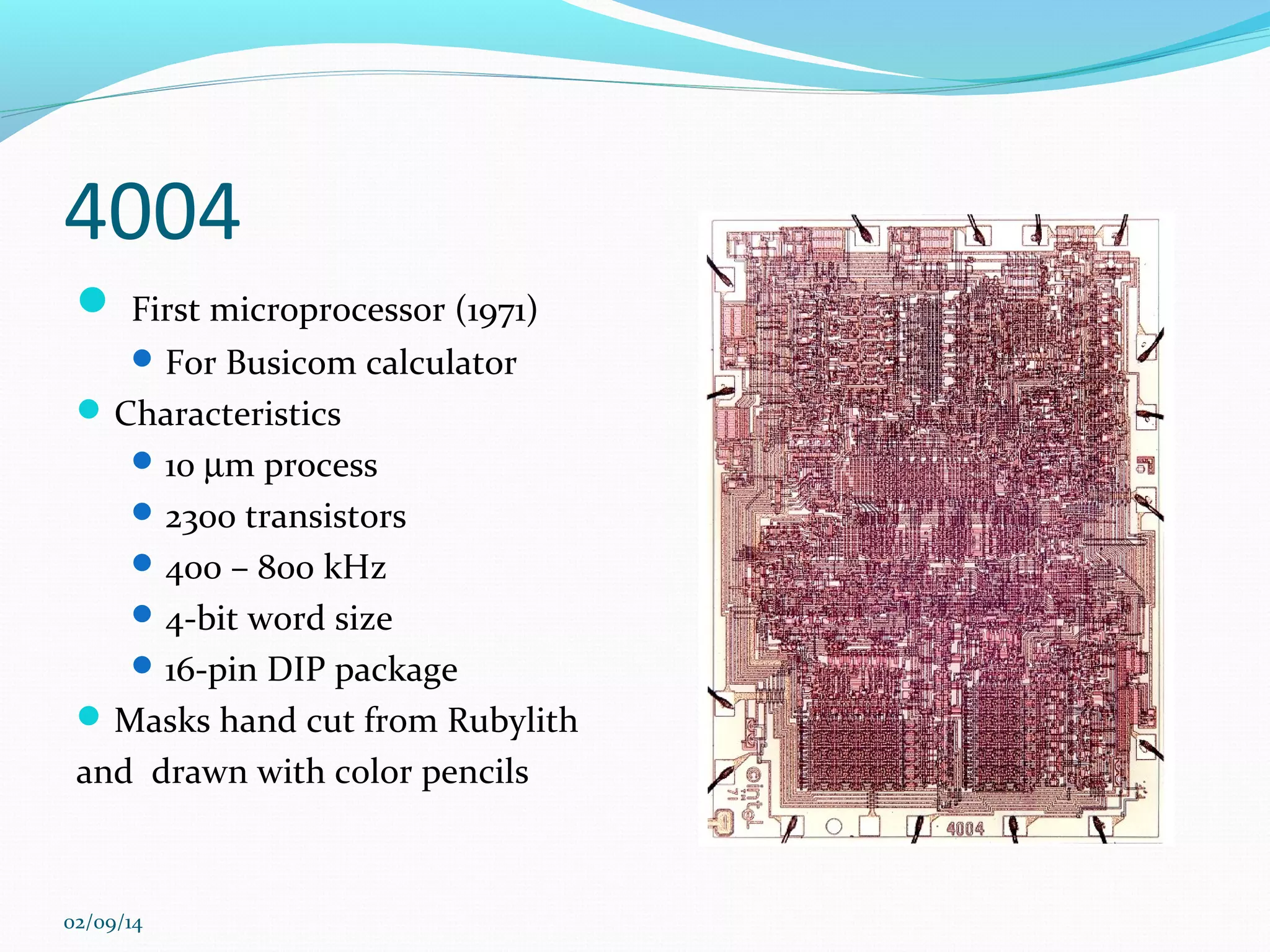
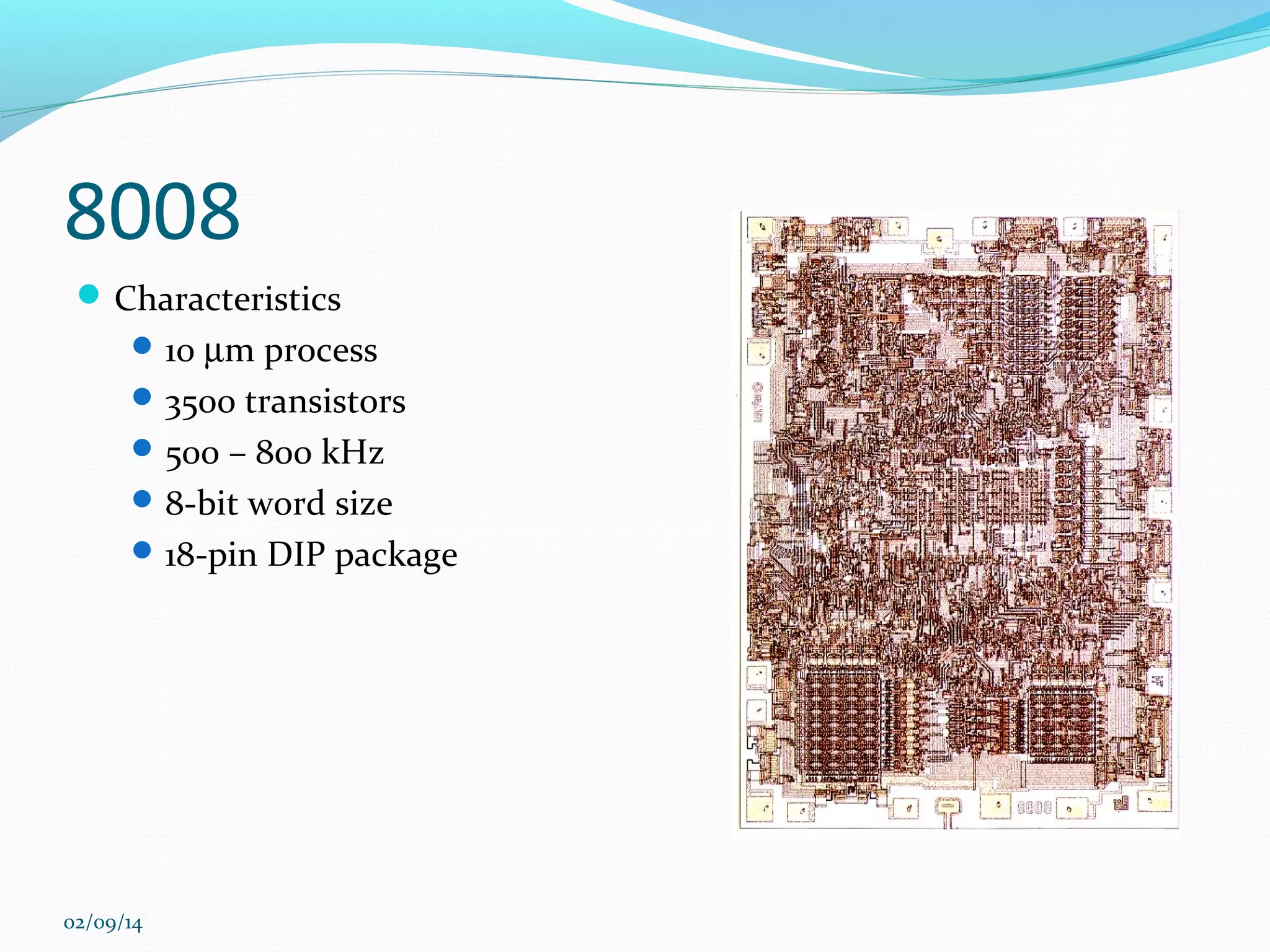
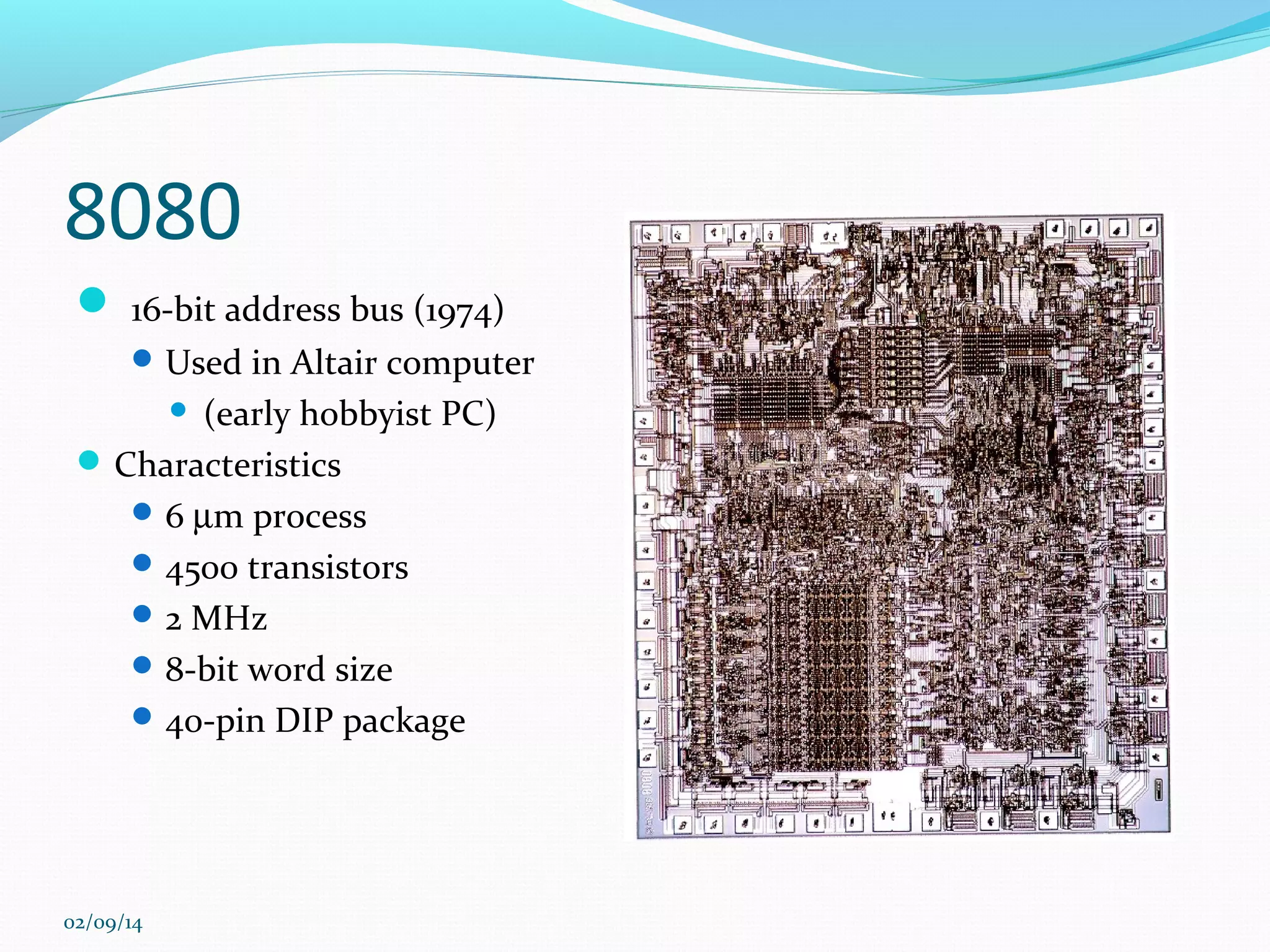
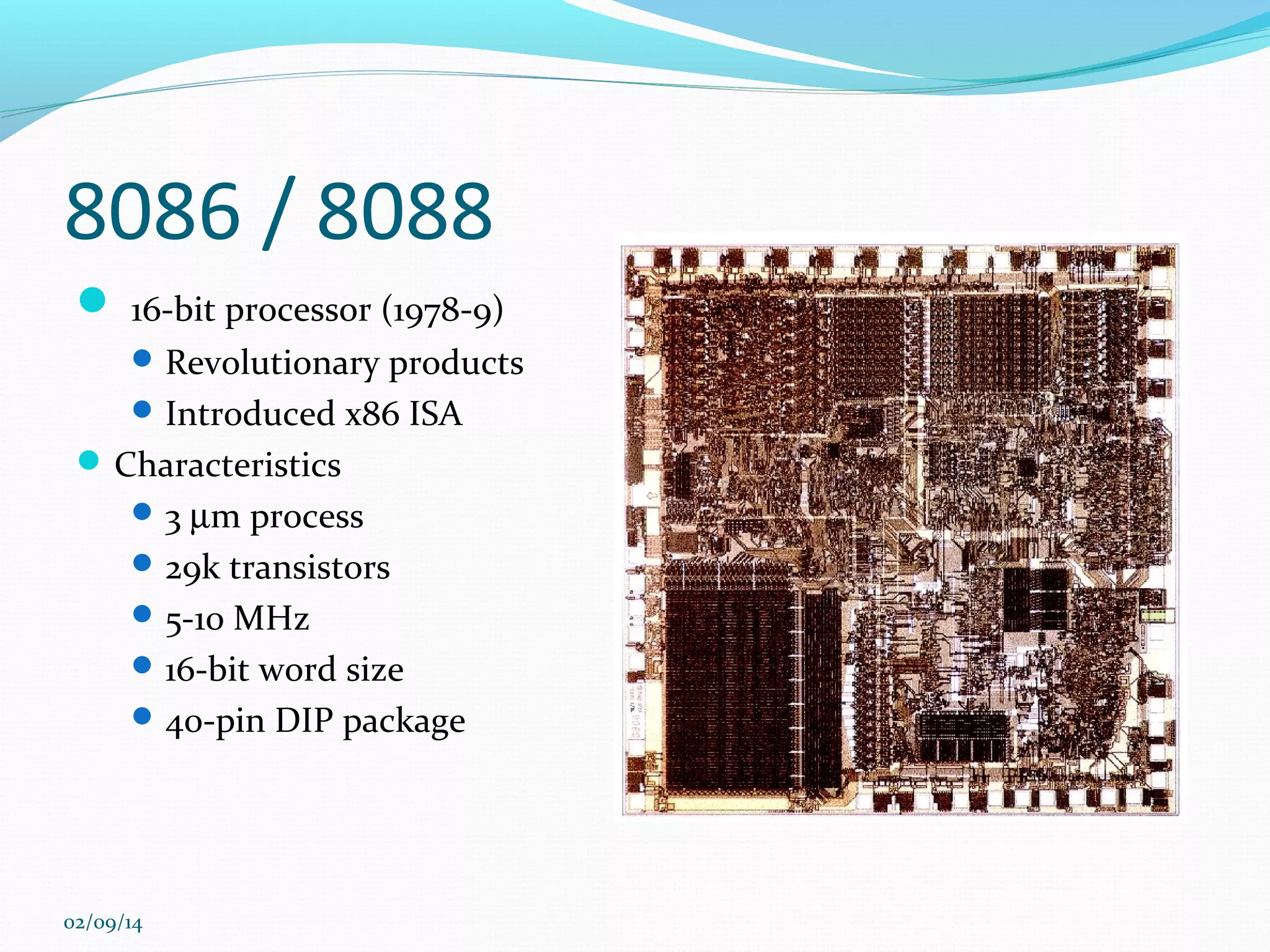
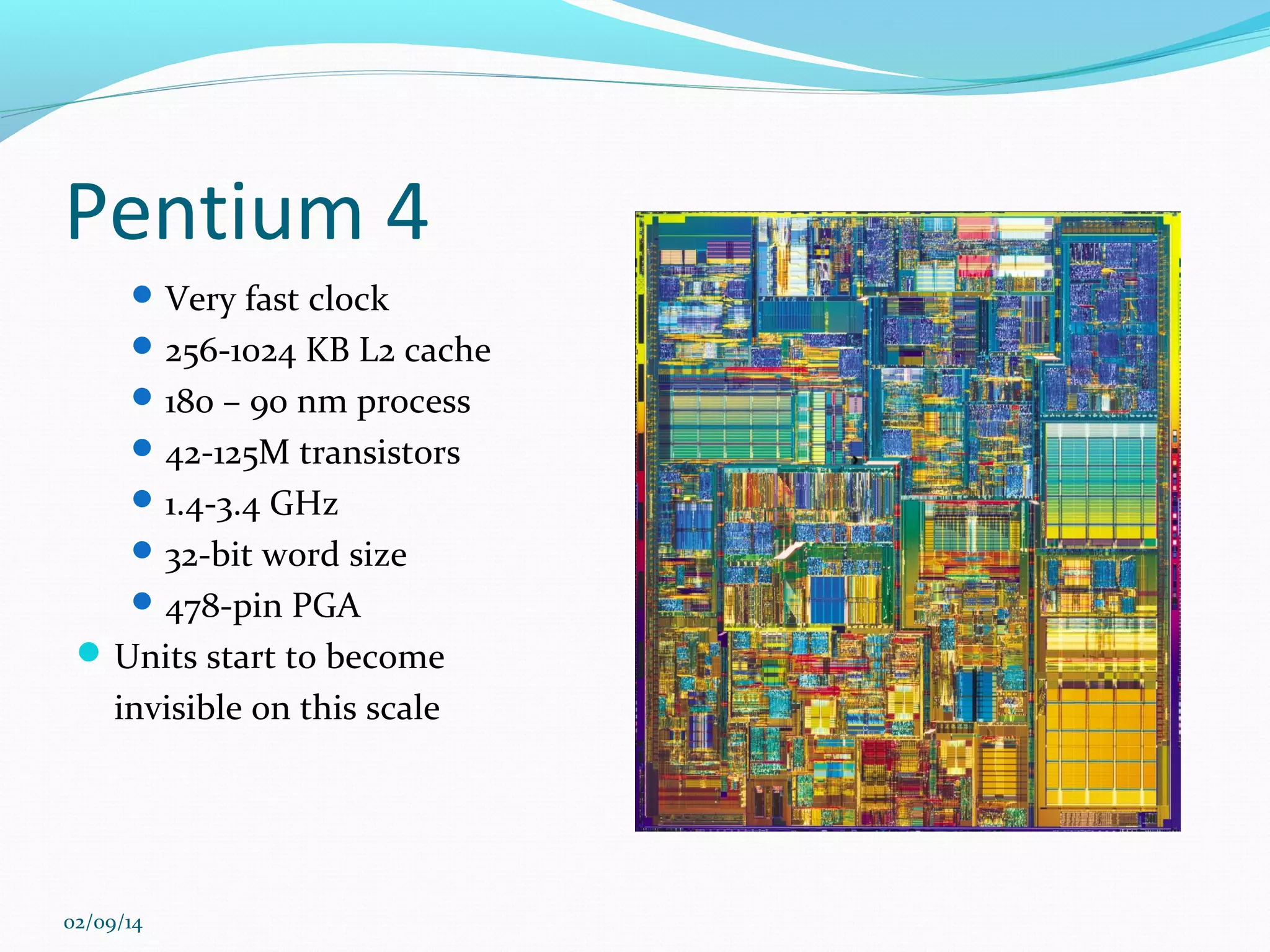
This document discusses integrated circuits and microprocessors. It begins by defining an integrated circuit as a set of electronic circuits on a semiconductor substrate and notes they are used in virtually all electronics. It then covers the invention of the integrated circuit by Jack Kilby and Robert Noyce, types of integrated circuits including analog, digital and mixed signal, and the advantages of integrated circuits like lower cost and power. The document proceeds to discuss the evolution of Intel microprocessors from the 4004 in 1971 to today's multi-core processors. It also outlines Moore's Law predicting transistor counts would double every year or two and how System on Chips are now commonly used in smartphones.






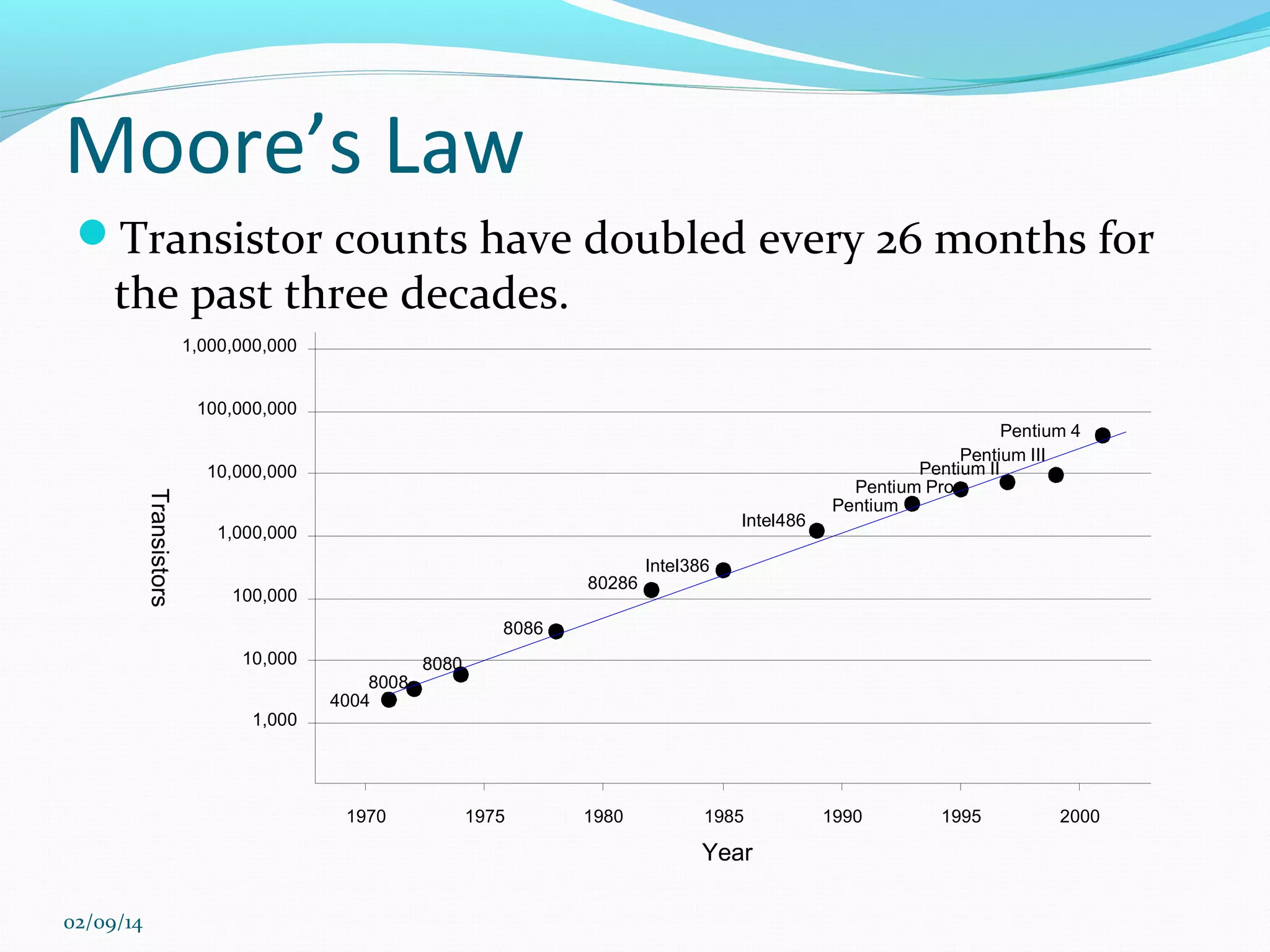
![Moore’s Law
In 1965, Gordon Moore predicted the exponential
growth of the number of transistors on an IC
Transistor count doubled
every year since invention
Predicted > 65,000
transistors by 1975!
Growth limited by power
[Moore65]
02/09/14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/psts016-140209013954-phpapp01/75/VLSI-Design-22-2048.jpg)