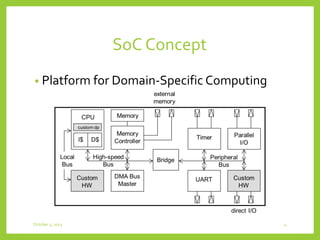
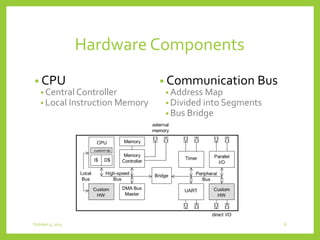
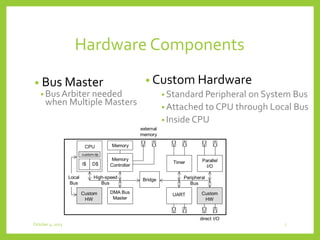
This document discusses system-on-chip (SoC) concepts, design principles, an example multimedia system, and the SoC design flow. It describes how SoCs integrate CPU, memory and custom hardware onto a single chip to improve efficiency. Key principles include distributed and heterogeneous processing, communications through multiple bus segments, and hierarchical control. An example portable multimedia SoC is presented with dedicated signal processing, general purpose processing and optimal parallelism control. The SoC design flow involves specification, design, validation and production.