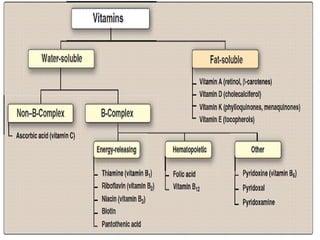
This document provides information about various vitamins in 3 sections:
1. It introduces vitamins and their classification as either water-soluble or fat-soluble.
2. Details are given for individual B vitamins, including their recommended daily intake, dietary sources, functions, and deficiency symptoms.
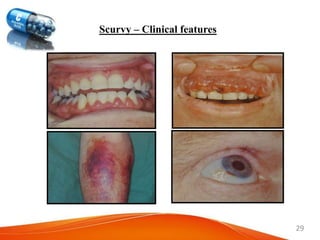
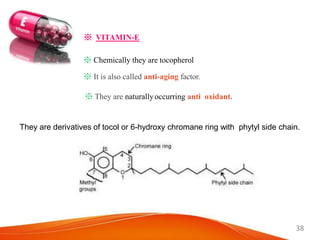
3. Fat-soluble vitamins A, D, and E are also described with their daily values, food sources, roles in the body, and health impacts of inadequacy.
![DEPARTMENT OF PERIODONTOLOGY & IMPLANTOLOGY
DR.MD.SHADAB ANWAR
M.M.D.C.H DARBHANGA
1ST YEAR PG STUDENT
(DEPARTMENT OF PERIODONTOLOGY)
------------------------------------------------------------------------
1
[ INTER- DEPARTMENTAL SEMINAR ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/final-201022090858/75/VITAMINS-1-2048.jpg)







































![44
REFRENCES:-
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vitamin
http://www.precisionnutrition.com/all-about-vitamins-
http://www.encyclopedia.com/topic/vitamin.aspx
Berdanier, C.D., & Berdanier, L. (2015). Advanced Nutrition: Macronutrients, Micronutrients,
and Metabolism, Second Edition. Oakville: CRC Press. Gropper, S.A., Smith, J.L., & Carr,
T.P. (2018).
Advanced Nutrition and Human Metabolism, Seventh Edition. Boston, MA: Cengage
Learning. Stipanuk, M.H., & Caudill, M.A. (2018).
Biochemical, Physiological, Molecular Aspects of Human Nutrition, Fourth Edition. St.
Louis, MO: Elsevier. Duyff R.L. (2017).
Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics Complete Food and Nutrition Guide, Fifth Edition.
Boston: Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. National Institute of Health (2018).
[U Satyanarayana] Biochemistry](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/final-201022090858/85/VITAMINS-44-320.jpg)
