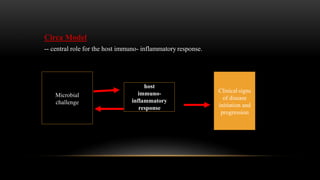
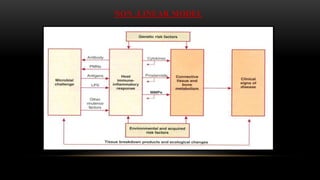
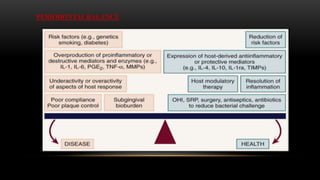
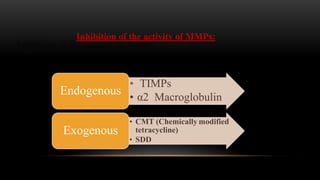
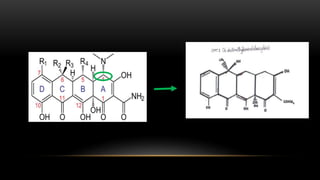
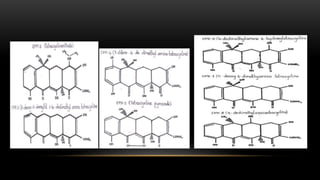
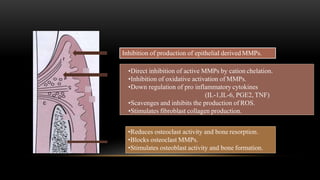
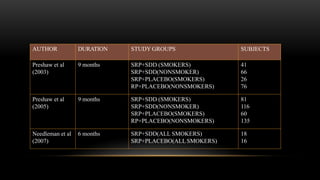
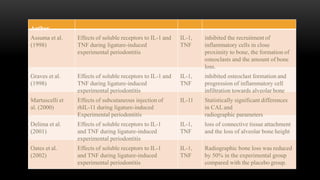
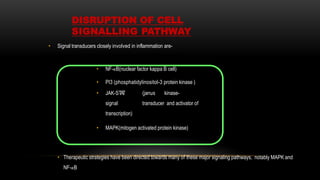
This document provides an overview of host modulation therapy for the treatment of periodontitis. It begins with definitions of key terms and a brief history of the development of the concept of host modulation. The pathogenesis of periodontitis and the host response are then described, focusing on the roles of inflammatory mediators like prostaglandins and matrix metalloproteinases in tissue destruction. The remainder of the document discusses various agents that can be used for host modulation therapy, including NSAIDs, tetracyclines, bisphosphonates, and their mechanisms of action in modulating the host response to reduce periodontal tissue breakdown.