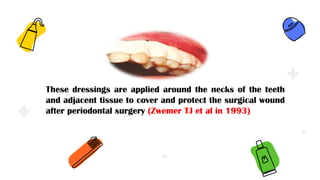
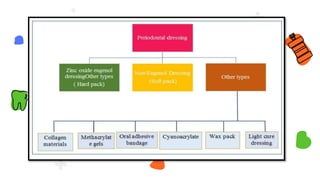
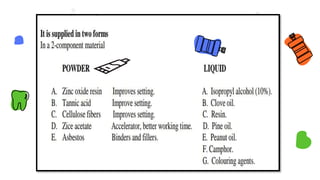
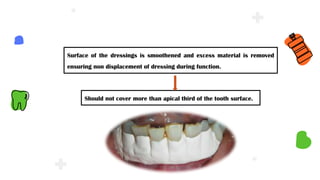
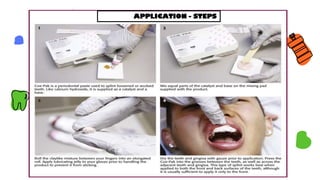
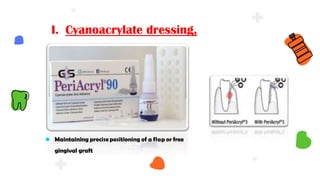
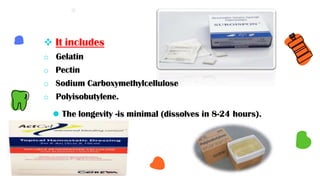
This document discusses different types of periodontal dressings used after periodontal surgery. It begins by describing the purpose of periodontal dressings in protecting healing tissues from forces during chewing. It then discusses the key properties dressings should have and lists three categories: those containing zinc oxide and eugenol, those containing zinc oxide without eugenol, and those containing neither. The document focuses on the composition, advantages, and application techniques of various common dressing types, including zinc oxide eugenol dressings, non-eugenol zinc oxide dressings like Coe-Pak, and alternatives like collagen dressings.