This document provides information on vitamin A, including its chemical forms and functions. Key points:
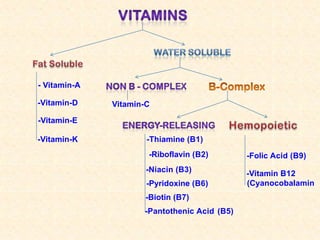
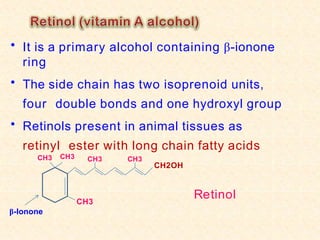
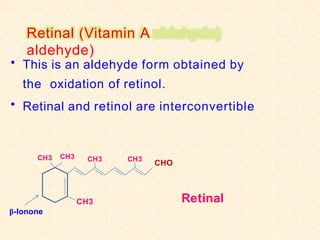
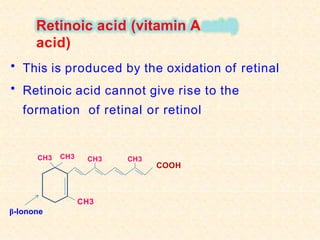
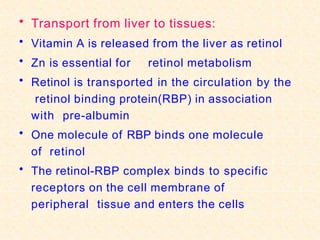
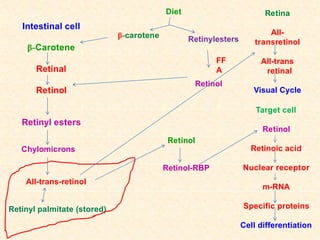
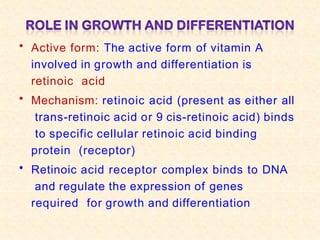
- Vitamin A exists in retinol, retinal, and retinoic acid forms which are fat-soluble and important for vision, cell growth, and immune function.
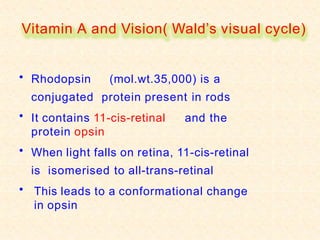
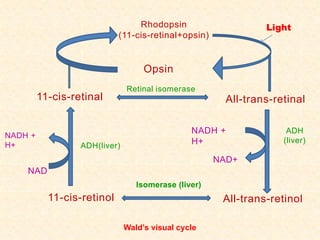
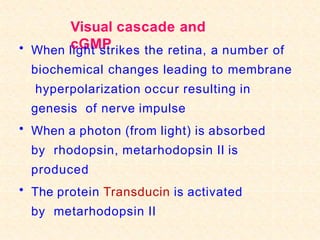
- The visual cycle involves rhodopsin (retinal bound to opsin) converting light to nerve signals in the retina.
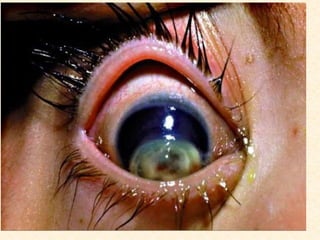
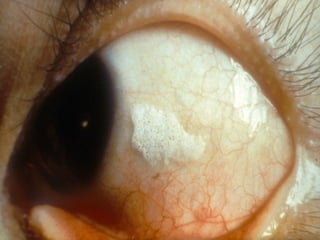
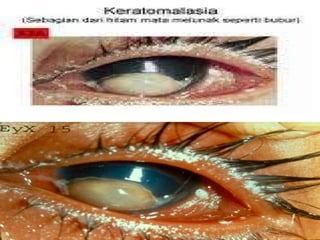
- Vitamin A supports epithelial cell integrity, immune function, reproduction, and is important for preventing deficiencies like night blindness.
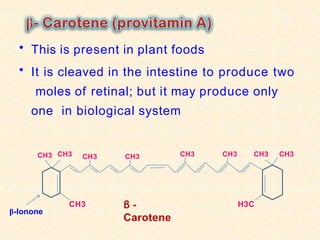
- Dietary sources include liver, dairy, eggs, yellow/green vegetables and fruits like carrots which contain provitamin A carotenoids.