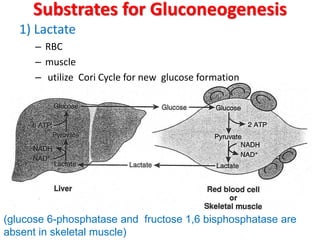
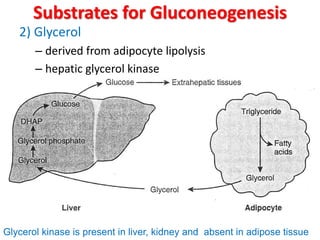
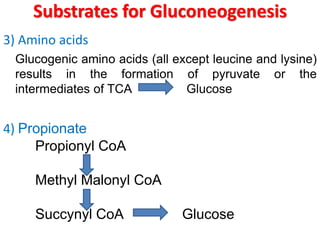
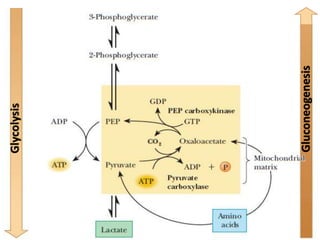
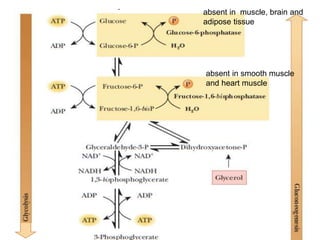
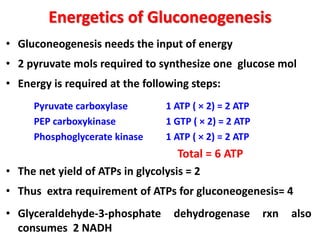
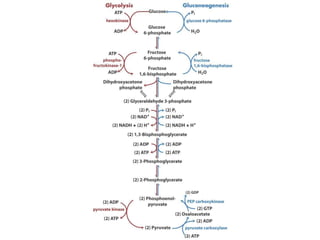
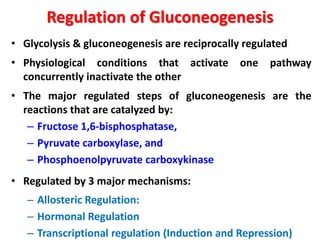
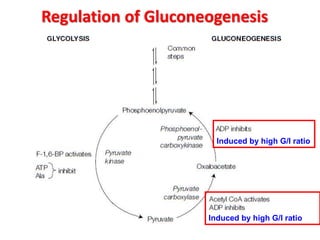
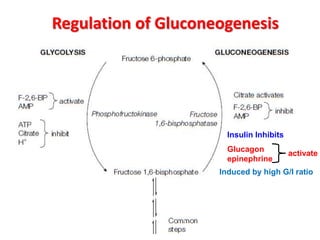
This document discusses gluconeogenesis, which is the formation of glucose from non-carbohydrate precursors in the liver and kidneys. Gluconeogenesis is important for maintaining blood glucose levels during periods of fasting or low carbohydrate intake. It involves 10 enzymatic steps, with 7 reversing the reactions of glycolysis. The key substrates used for gluconeogenesis include lactate, glycerol, certain amino acids, and intermediates of the citric acid cycle. Gluconeogenesis is regulated by hormones like insulin and glucagon, as well as feedback inhibition based on energy levels and metabolite concentrations.