Embed presentation
Downloaded 779 times



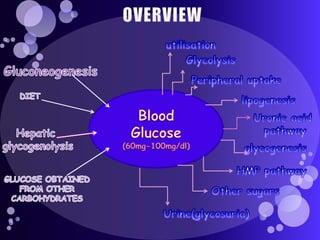


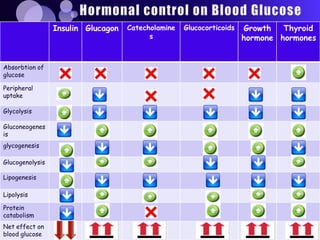
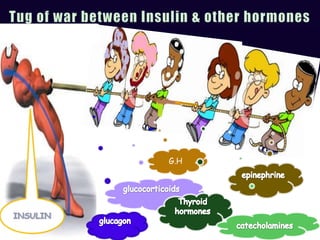
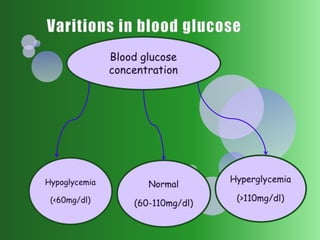



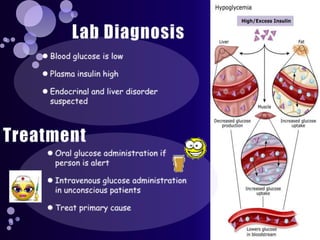

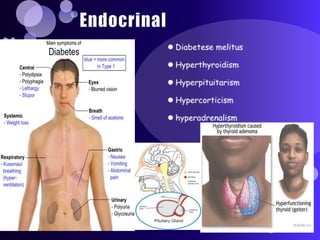
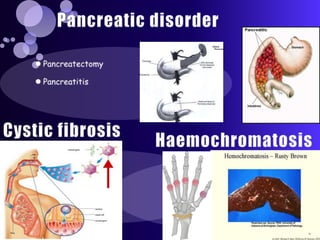





The document summarizes key topics in biochemistry including the regulation of blood glucose, hormonal control of blood glucose, hypoglycemia and its clinical aspects, hyperglycemia and its clinical aspects. It also includes diagrams of glucose metabolism pathways and effects of various hormones like insulin and glucagon on blood glucose levels. Tables outline the clinical manifestations of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia. In conclusion, it provides an overview of important biochemistry concepts and regulatory mechanisms related to blood glucose homeostasis.





























