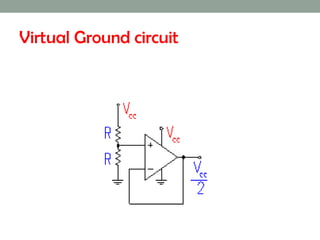
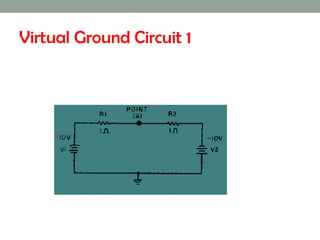
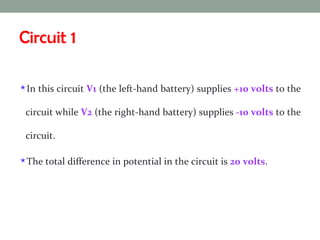
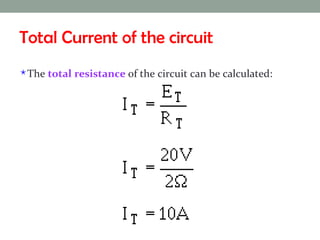
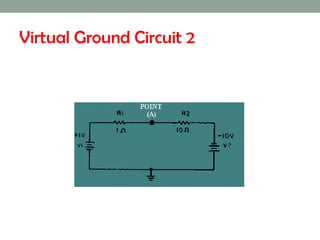
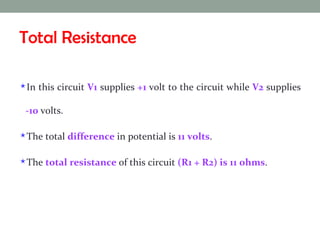
A virtual ground is a point in a circuit that has a voltage of 0 volts, but is not directly connected to ground. The document describes two virtual ground circuits using voltage dividers with opposing voltage sources. In the first circuit, the 10V and -10V sources create a 20V difference with a virtual ground at the midpoint. In the second circuit, the 1V and -10V sources create an 11V difference, with the virtual ground again occurring at the midpoint.