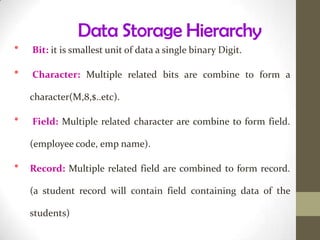
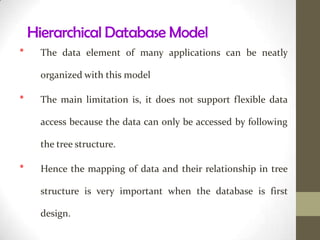
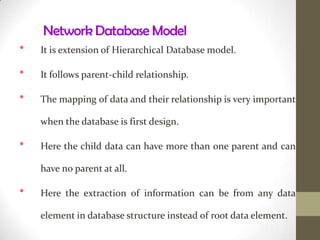
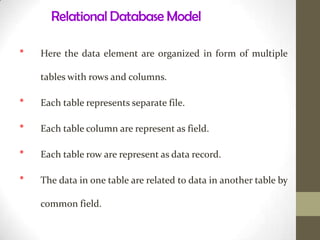
This document discusses the basics of database management systems (DBMS). It begins by explaining the data storage hierarchy from the bit level up to the database level. It then covers different database models including hierarchical, network, relational, and object-oriented. Key components of a DBMS like DDL, DML, query language, and report generators are defined. Commercial DBMS examples are provided. The document concludes with an overview of creating and using a database, including defining the structure, entering data, and searching for information.