Embed presentation
Download to read offline





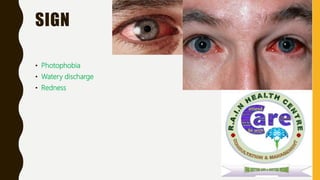




Viral conjunctivitis is a common form of pink eye that is highly contagious and spread through sneezing, coughing, or contact with infected individuals or surfaces. It causes watery discharge from the eye, redness, burning, and light sensitivity. While self-limiting, it can be treated with cool compresses, artificial tears, and antihistamines to relieve symptoms until it runs its course. Proper hand washing and avoiding sharing towels or touching the eyes can help prevent spreading the infection.








