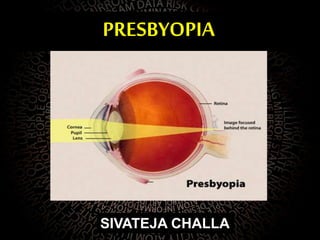
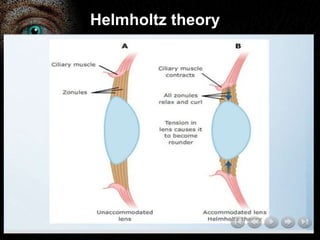
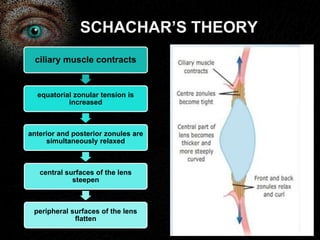
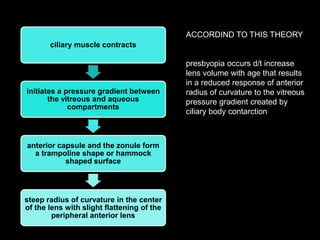
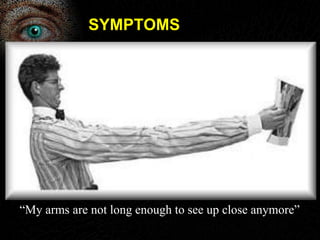
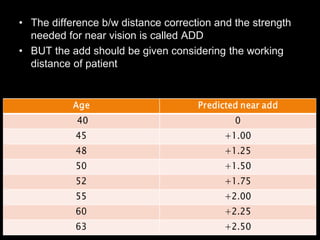
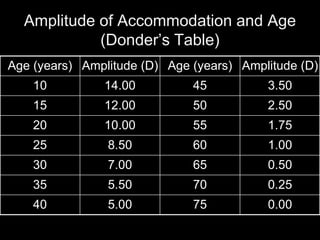
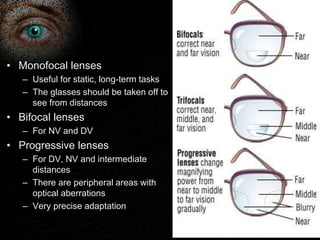
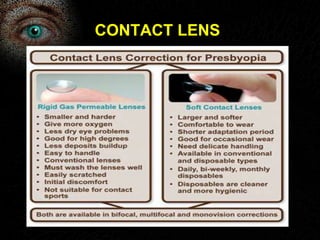
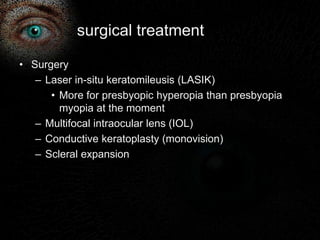
Presbyopia is the loss of accommodation ability that occurs with aging. It results from a loss of elasticity in the lens and ciliary muscles. By age 40-45, most people experience difficulty seeing objects close up. Symptoms include problems with near vision that are worse in low light. It is diagnosed by reduced amplitude of accommodation. Treatment involves using reading glasses, bifocals, or progressive lenses to add the needed optical power for near vision. Multifocal contact lenses and refractive surgery can also help treat presbyopia.