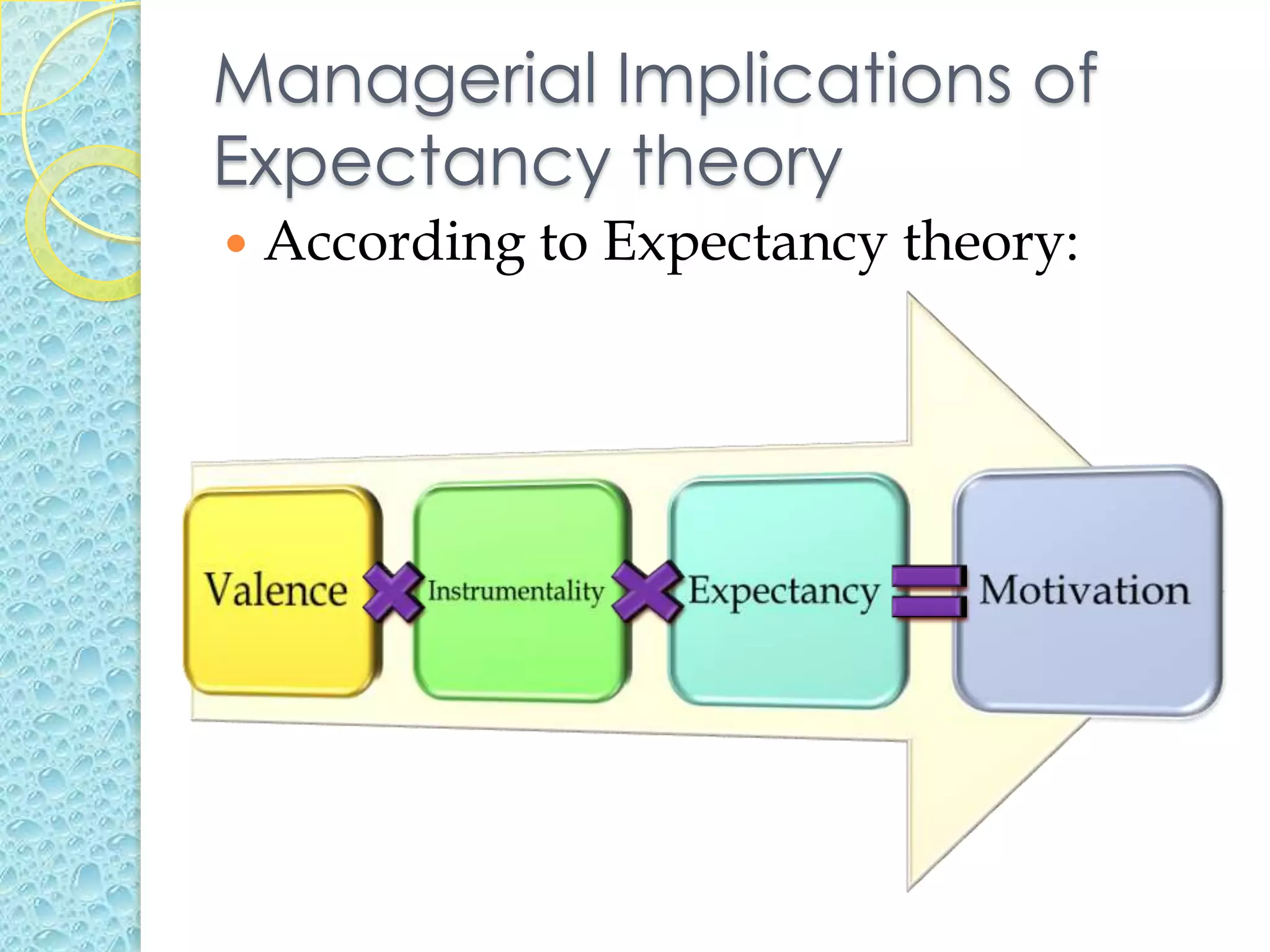
Some employees are motivated to go to work during a snowstorm because they have high expectancy, instrumentality, and valence. Employees with high expectancy believe that with effort they can complete their tasks. Those with high instrumentality believe good performance will lead to rewards. Employees with high valence highly value the potential rewards. Other employees do not go to work because they lack one or more of these factors. They may not believe effort will lead to good performance, that performance connects to rewards, or that rewards are worthwhile. According to expectancy theory, motivation is highest when all three factors - expectancy, instrumentality, and valence - are high.