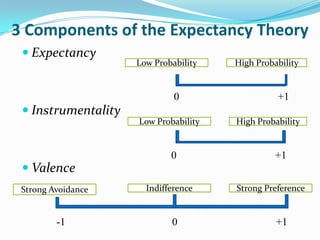
This document provides an overview of Expectancy Theory, including its key components and relevance to organizational behavior. Expectancy Theory proposes that individuals will be motivated to put forth effort if they believe it will lead to good performance and rewards. The theory has three components: Expectancy (effort leads to performance), Instrumentality (performance leads to rewards), and Valence (rewards are desirable). The document outlines Victor Vroom's contributions to developing Expectancy Theory and explains how management can apply it by understanding employee needs, ensuring promised rewards are given, and recognizing what employees value.