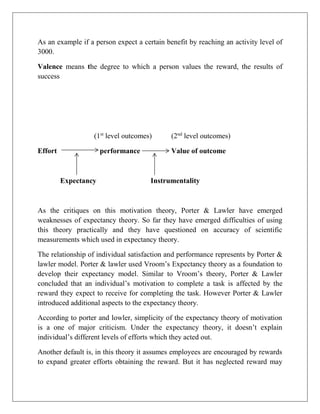
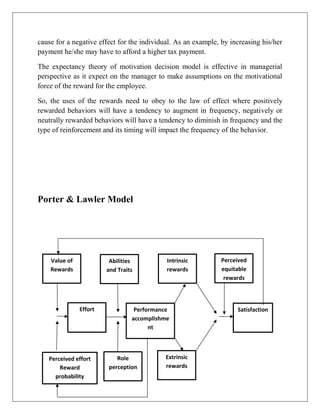
Expectancy theory is a motivation theory proposed by Victor Vroom that explains how individuals choose between alternatives that vary in their expected consequences. The theory states that motivation is a function of Expectancy (the belief that effort will lead to performance), Instrumentality (the belief that performance will lead to rewards), and Valence (the value placed on the rewards). Porter and Lawler expanded on the theory by introducing additional factors like abilities, individual satisfaction, and reward equity that influence motivation. While expectancy theory provides insights, it has also received critiques for oversimplifying motivation and difficulties accurately measuring scientific concepts.