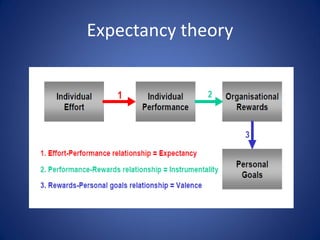
Expectancy theory is a motivation theory that states individuals are motivated if they believe good performance will lead to desired outcomes. It was first proposed by Victor Vroom and includes three variables: expectancy, the belief that effort will lead to performance; instrumentality, the belief performance will lead to rewards; and valence, the value placed on rewards. The theory emphasizes relating rewards directly to performance and ensuring rewards are deserved. Factors like skills, support, resources, and information impact expectancy perceptions. Vroom introduced these variables to explain how motivation is created psychologically through individuals' beliefs about expectancy, instrumentality, and valence interacting.






![Valence
• It refers to the emotional orientations which people
hold with respect to rewards.
• The depth of the want of an employee for extrinsic
[money, promotion, free time, benefits] or intrinsic
[satisfaction] rewards.
• Management must discover what employees
appreciate. For the valence to be positive, the person
must prefer attaining the outcome to not attaining it.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/expectancytheory-copy-120610122832-phpapp01/85/Expectancy-theory-7-320.jpg)