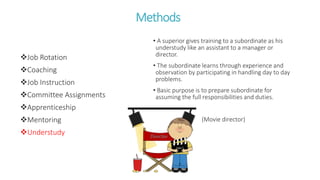
The document discusses various on-the-job training methods including learning through observation, job rotation, coaching, and apprenticeships. These methods are aimed at providing practical experience while minimizing costs and disruptions. Additionally, the advantages and disadvantages of each method are outlined, emphasizing immediate feedback, motivation, and potential safety hazards.