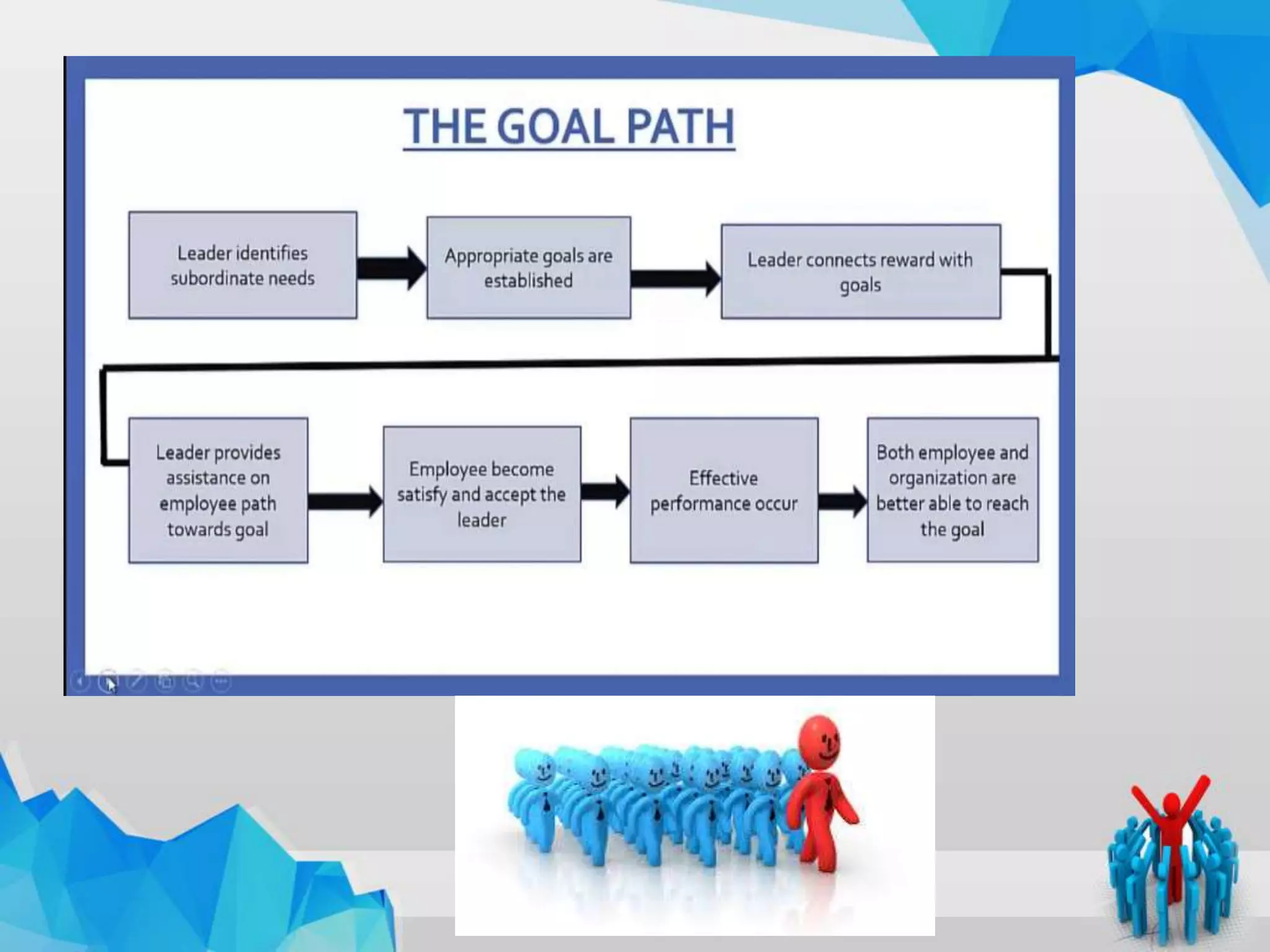
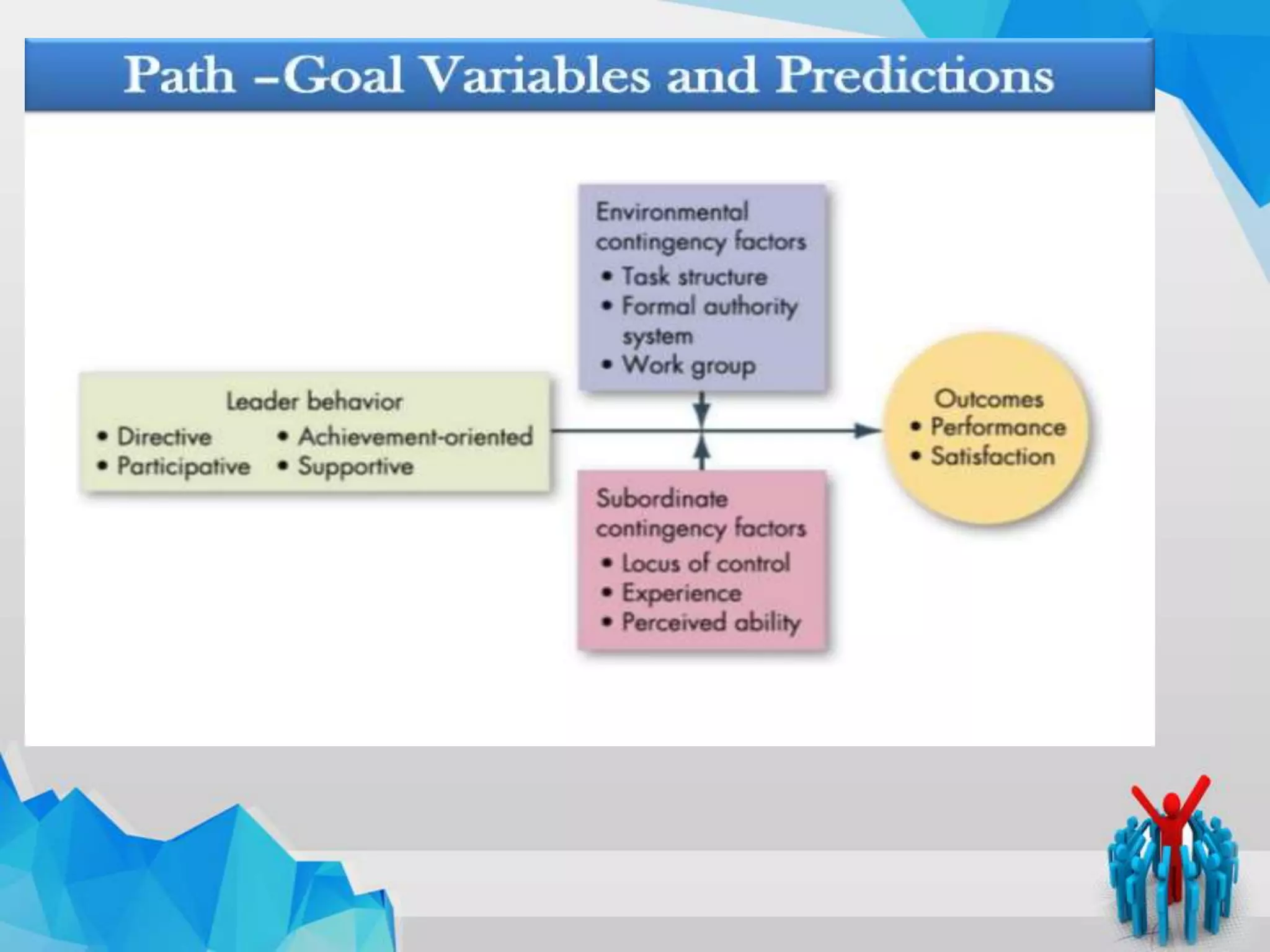
The document summarizes Robert House's path-goal leadership theory. The theory proposes that a leader's main functions are to clarify goals, provide a path to achieving goals, and remove obstacles. A leader's style (directive, supportive, participative, or achievement-oriented) depends on subordinate and environmental characteristics. The theory aims to motivate subordinates by satisfying their needs and complementing the work environment with guidance and rewards. While it addresses motivation, the theory is complex and lacks research support. Overall, the path-goal model suggests leadership that reduces uncertainty for subordinates increases motivation and satisfaction.