Expectancy theory is a motivation theory proposed by Victor Vroom that says individuals are motivated to make choices that they believe will result in desirable outcomes. The theory is based on three variables: valence, which is the value an individual places on a reward; expectancy, which is an individual's belief that they are capable of performing to a level to attain a reward; and instrumentality, which is the belief that good performance will lead to an expected reward. According to expectancy theory, motivation is highest when an individual believes a reward is valuable, they are able to perform well enough to receive it, and that their performance will directly result in receiving the reward.




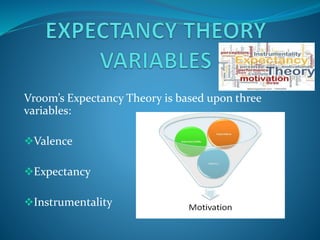
![“Is the outcome I get of any value to me?”.
It refers to the emotional orientations
which people hold with respect to outcomes
[rewards]. The depth of the want of an
employee for extrinsic [money, promotion,
free time, benefits] or intrinsic [satisfaction]
rewards.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/expectancytheory-150111171656-conversion-gate02/85/Expectancy-theory-6-320.jpg)


