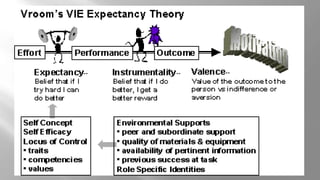
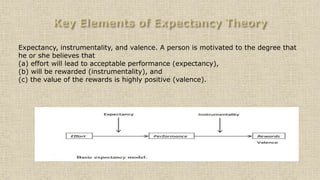
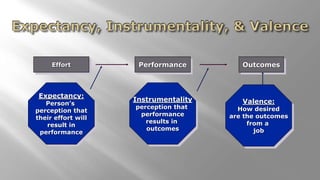
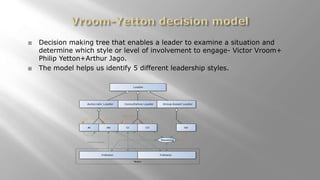
- Victor Vroom is a professor at Yale School of Management who developed expectancy theory of motivation.
- Expectancy theory states that motivation is based on the expectation that effort will lead to good performance, which will result in desired rewards.
- The theory emphasizes relating rewards directly to performance and ensuring recipients view rewards as deserved.