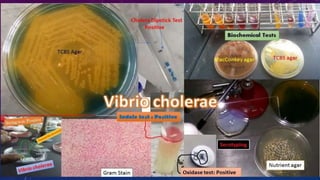
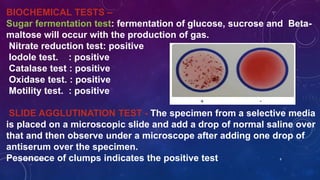
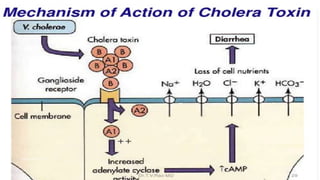
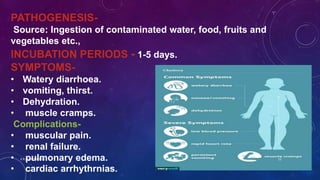
Vibrio cholerae is a gram-negative, curved bacillus that causes the disease cholera. It was discovered independently by Filippo Pacini in 1854 in Italy and Robert Koch in 1883 in India. Cholera is typically spread through contaminated water and causes severe diarrhea and dehydration. Modern water treatment has eliminated cholera in most developed countries, but it remains problematic in parts of Asia, Africa, and South America where water treatment is lacking. Diagnosis involves examining stool samples under a microscope for the presence of V. cholerae or culturing samples on selective media such as TCBS agar. Treatment focuses on oral rehydration therapy to replace lost fluids. Prevention involves drinking bottled water,