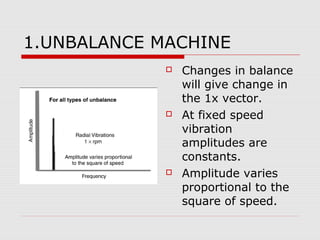
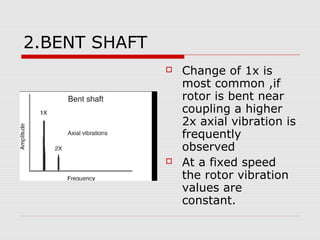
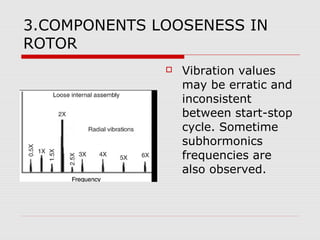
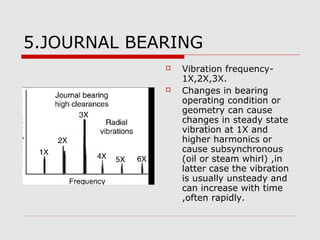
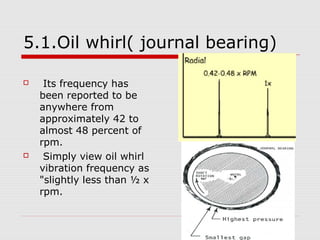
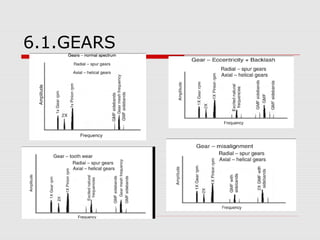
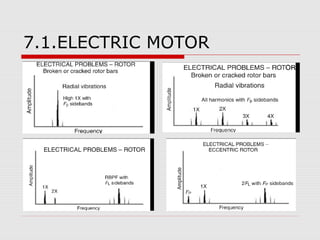
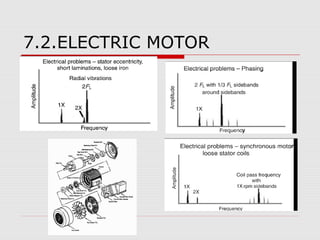
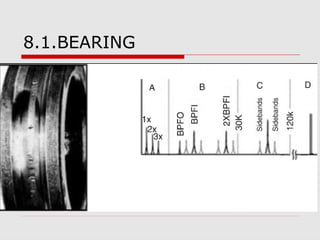
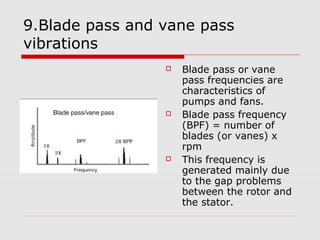
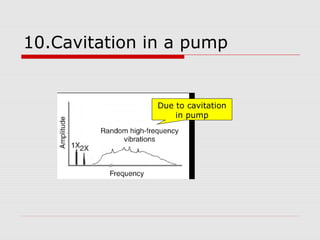
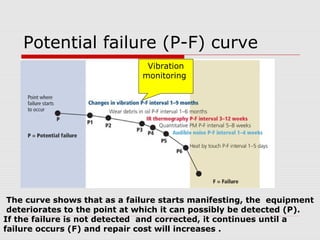
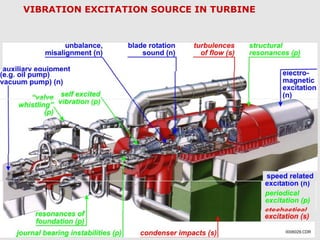
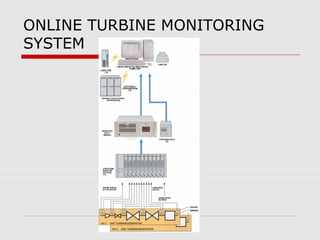
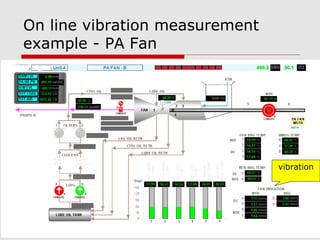
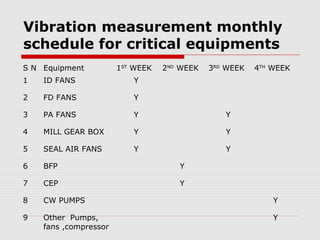
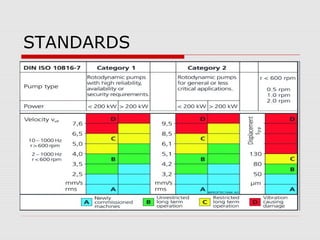
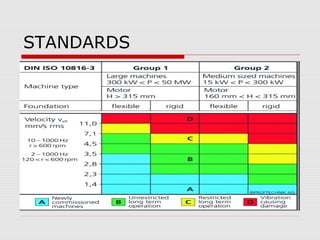
This document discusses vibration analysis at thermal power plants. It outlines the objectives of vibration monitoring, which include improving equipment protection, safety, maintenance procedures, and extending equipment life. Vibration monitoring measures characteristics like amplitude and frequency to identify abnormal conditions. Common defects that can be detected through vibration analysis are unbalance, misalignment, loose components, rotor rub, bearing issues, and blade/vane pass frequencies. Online monitoring systems are used at thermal plants to continuously monitor critical equipment like turbines, generators, and pumps to detect faults early and avoid failures. Standards provide guidelines for effective vibration analysis and maintenance.