The document discusses condition monitoring for steam turbines. It outlines several key points:
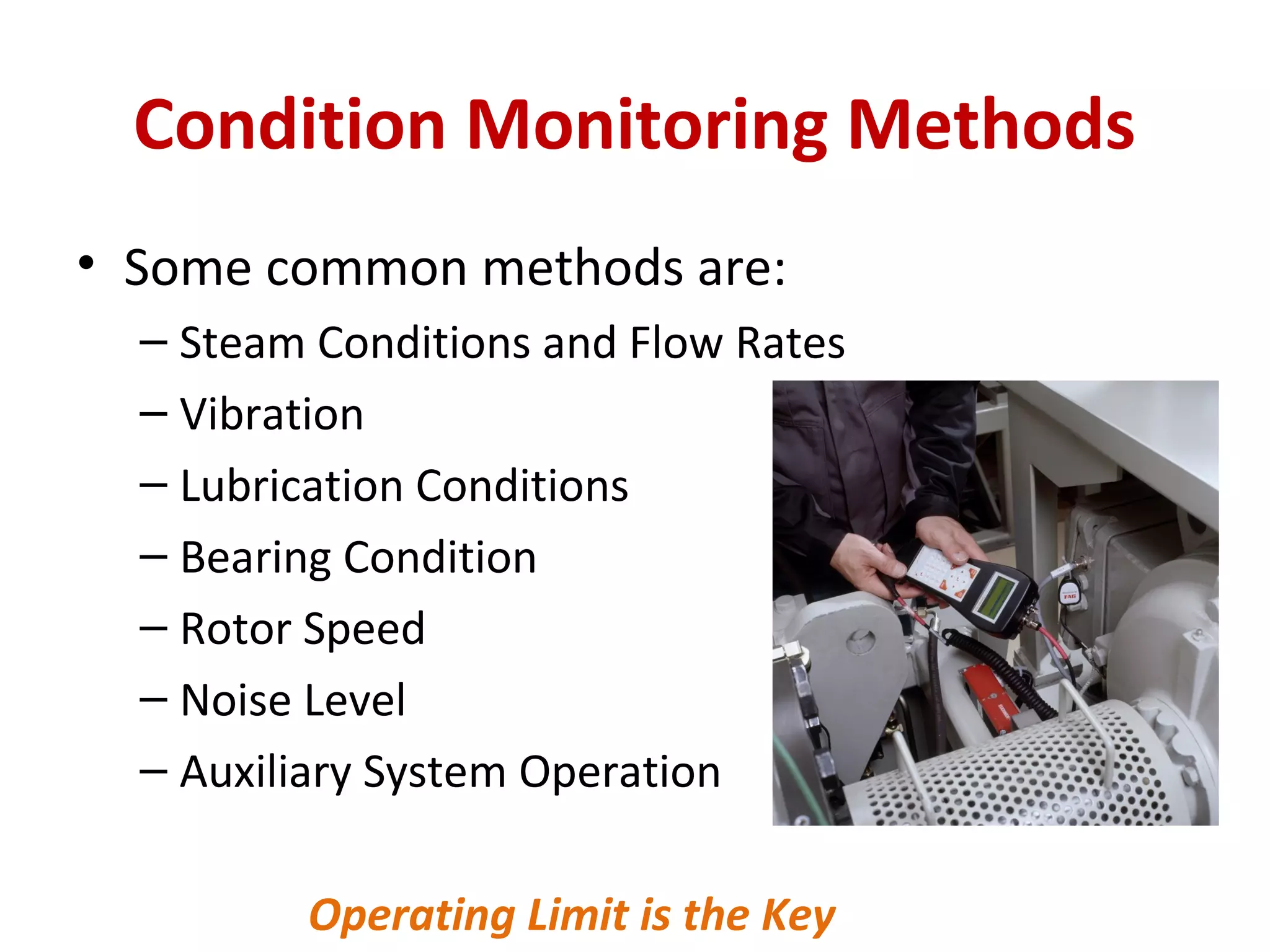
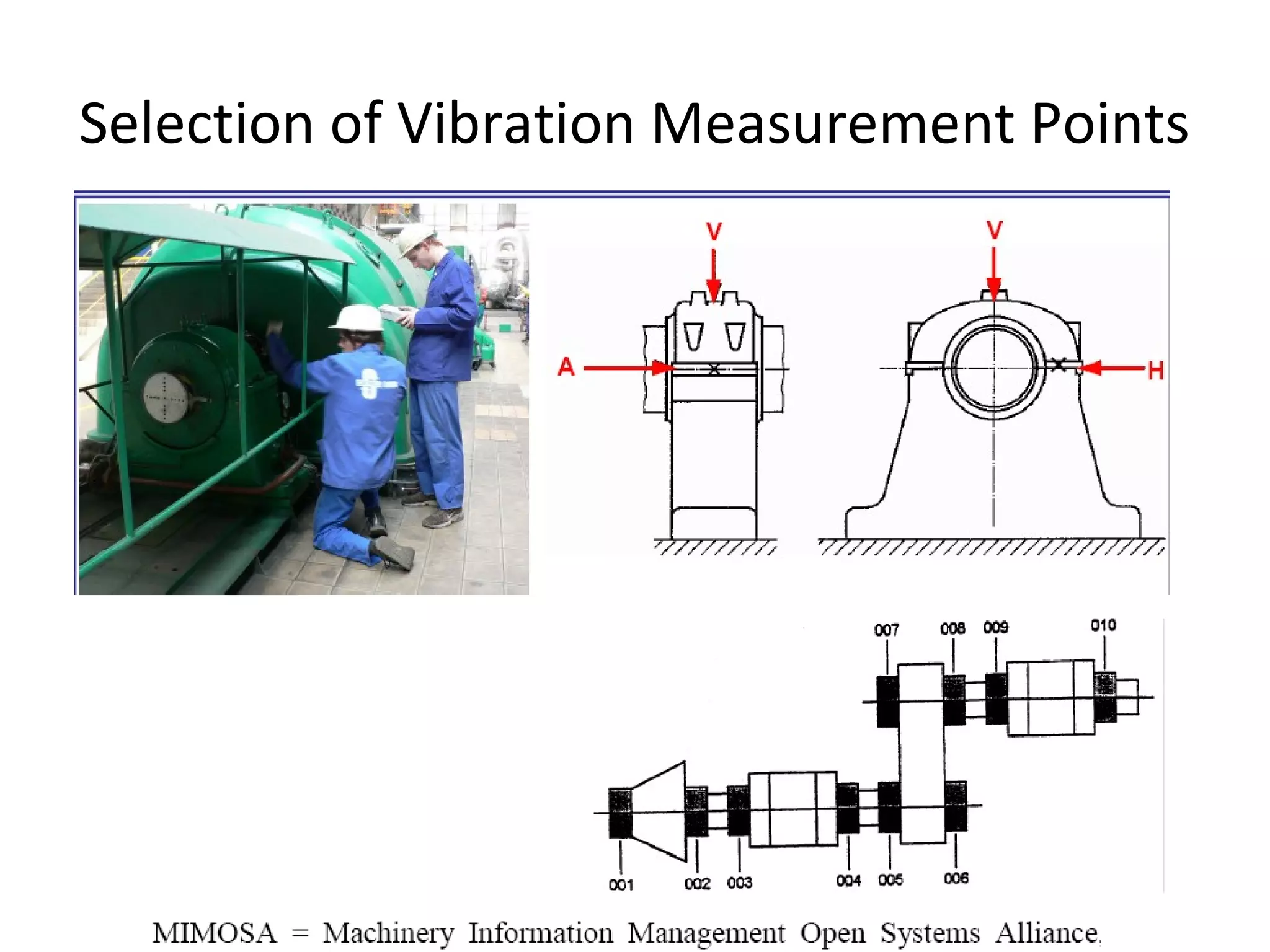
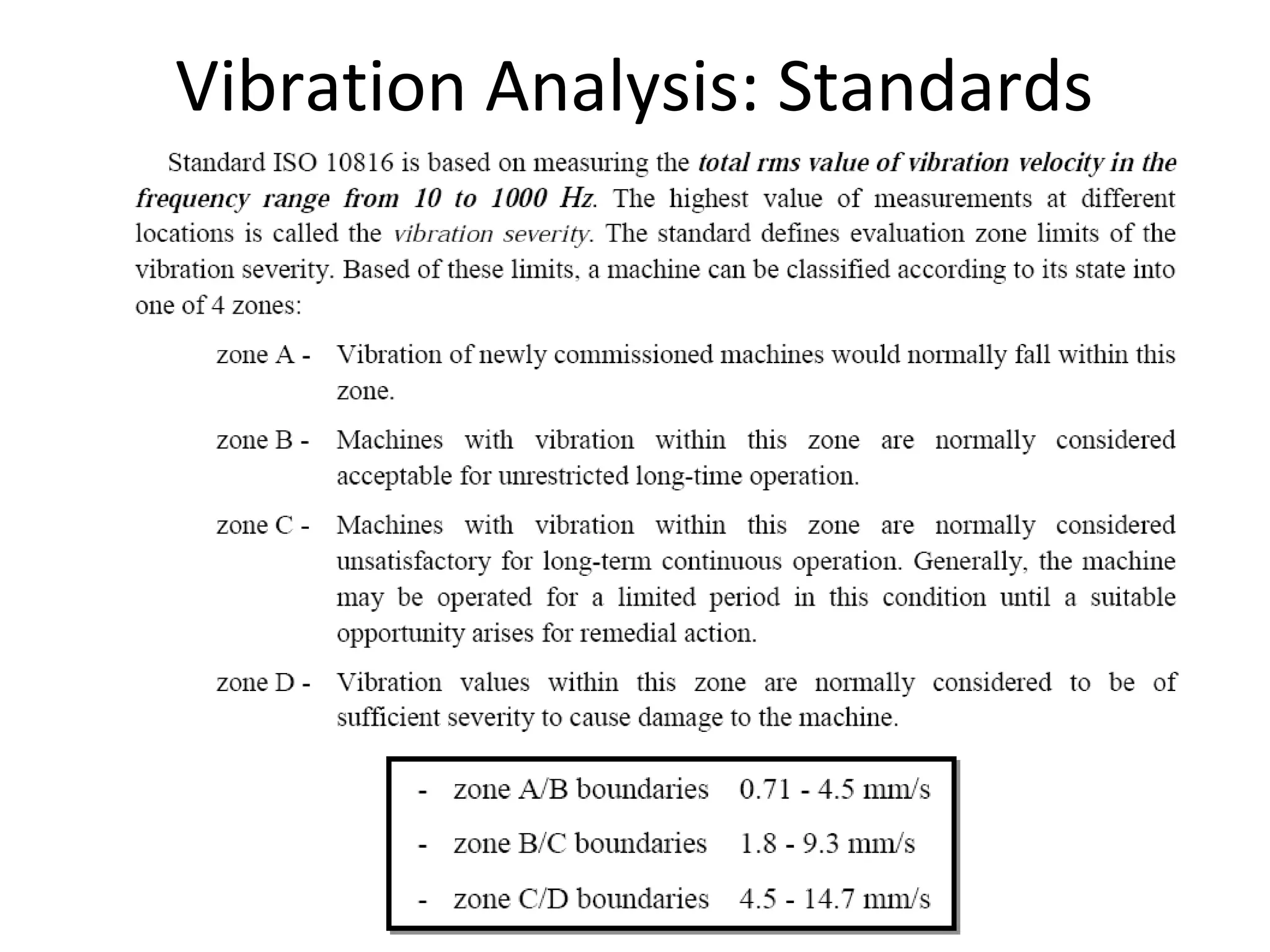
1. Condition monitoring methods for steam turbines include monitoring steam conditions and flow rates, vibration, lubrication conditions, bearing condition, rotor speed, noise levels, and auxiliary system operation.
2. Common failure modes of steam turbines include bearing failures from loss of lubrication or contamination, blade failures from foreign object damage or fatigue, and valve failures from solid particle damage or erosion.
3. Condition monitoring is important for identifying faults early to allow corrective action to save assets and avoid production losses. Monitoring methods help ascertain equipment condition while failure modes can be prevented through monitoring and preventive maintenance.