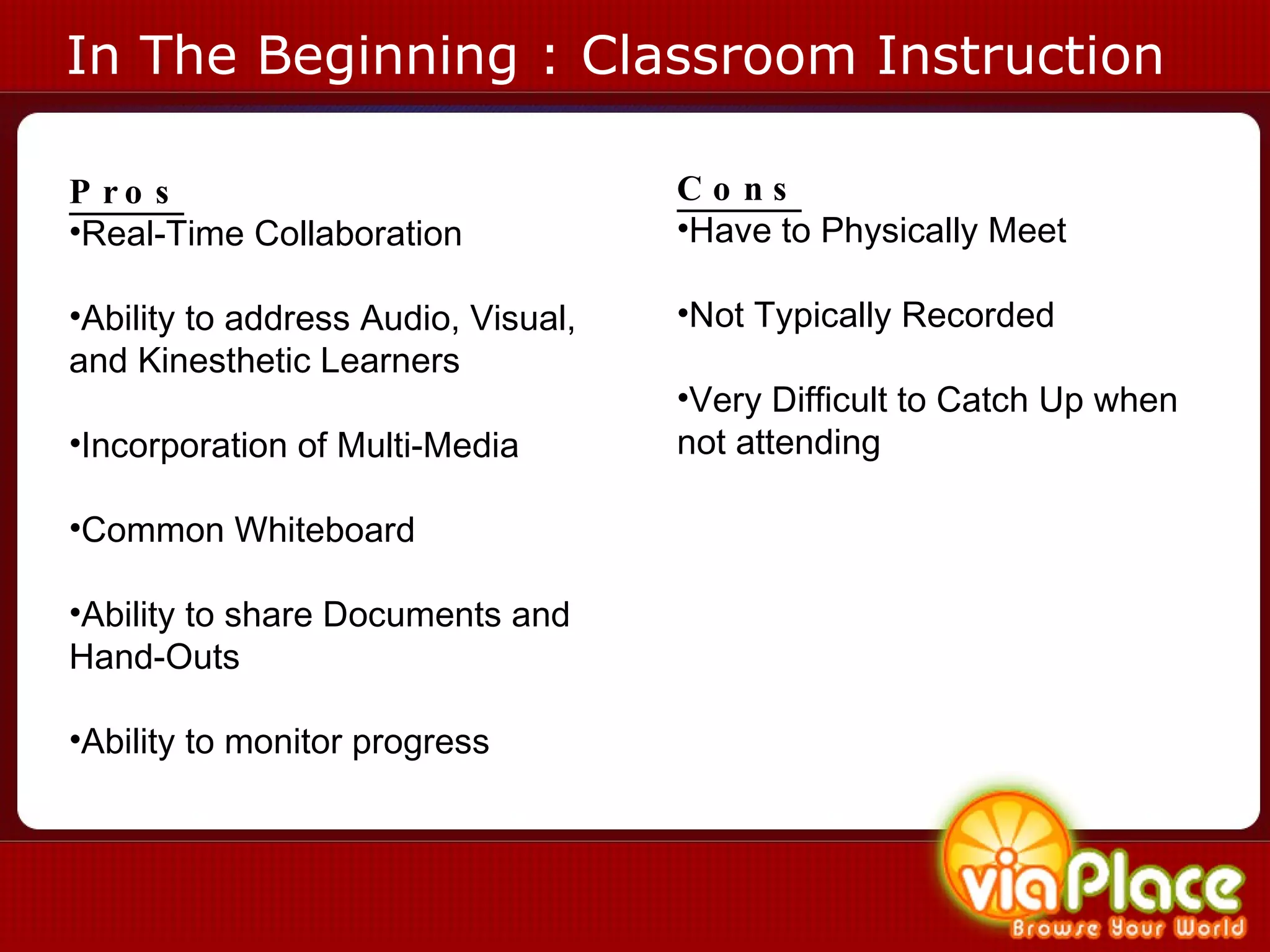
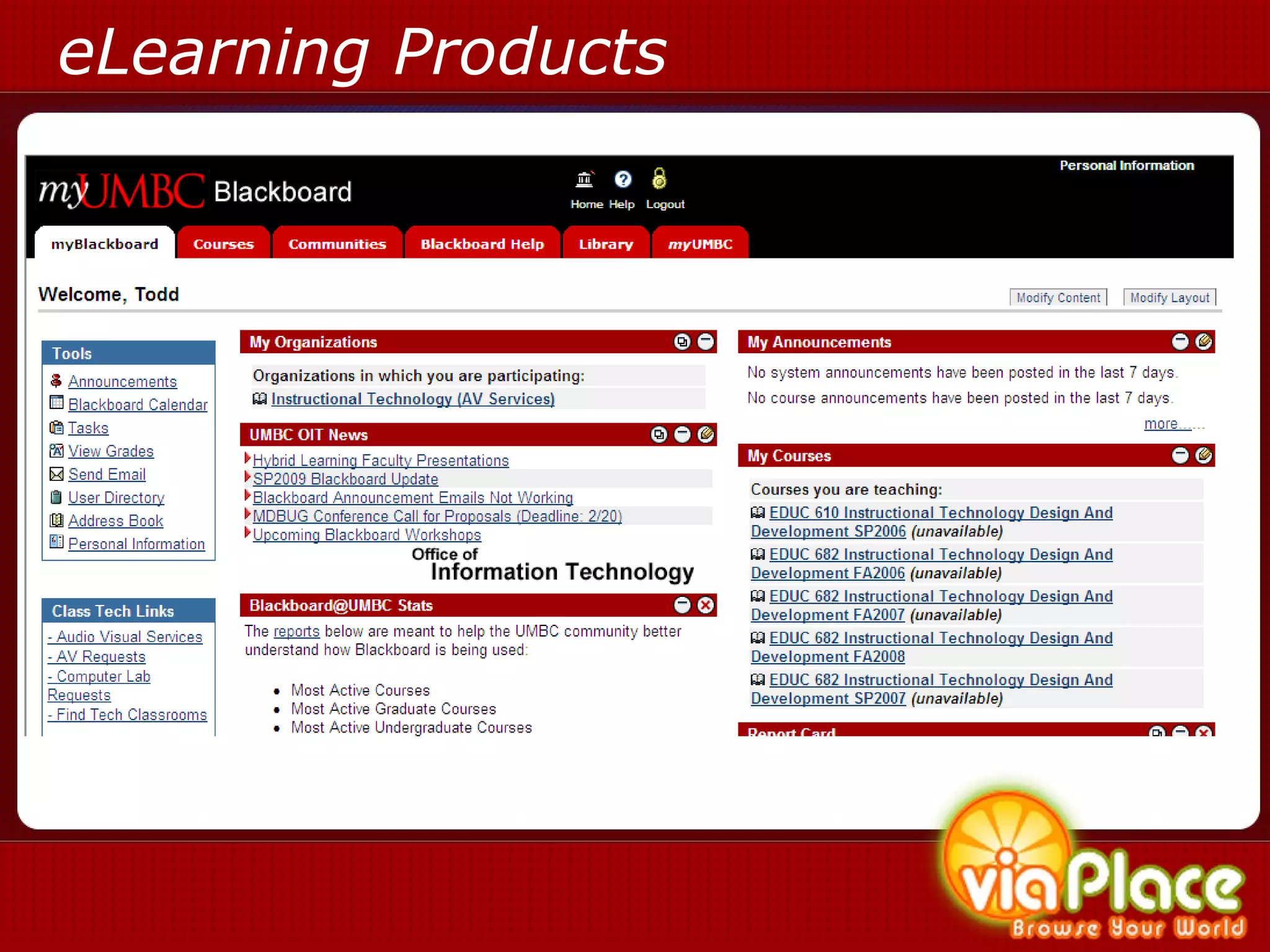
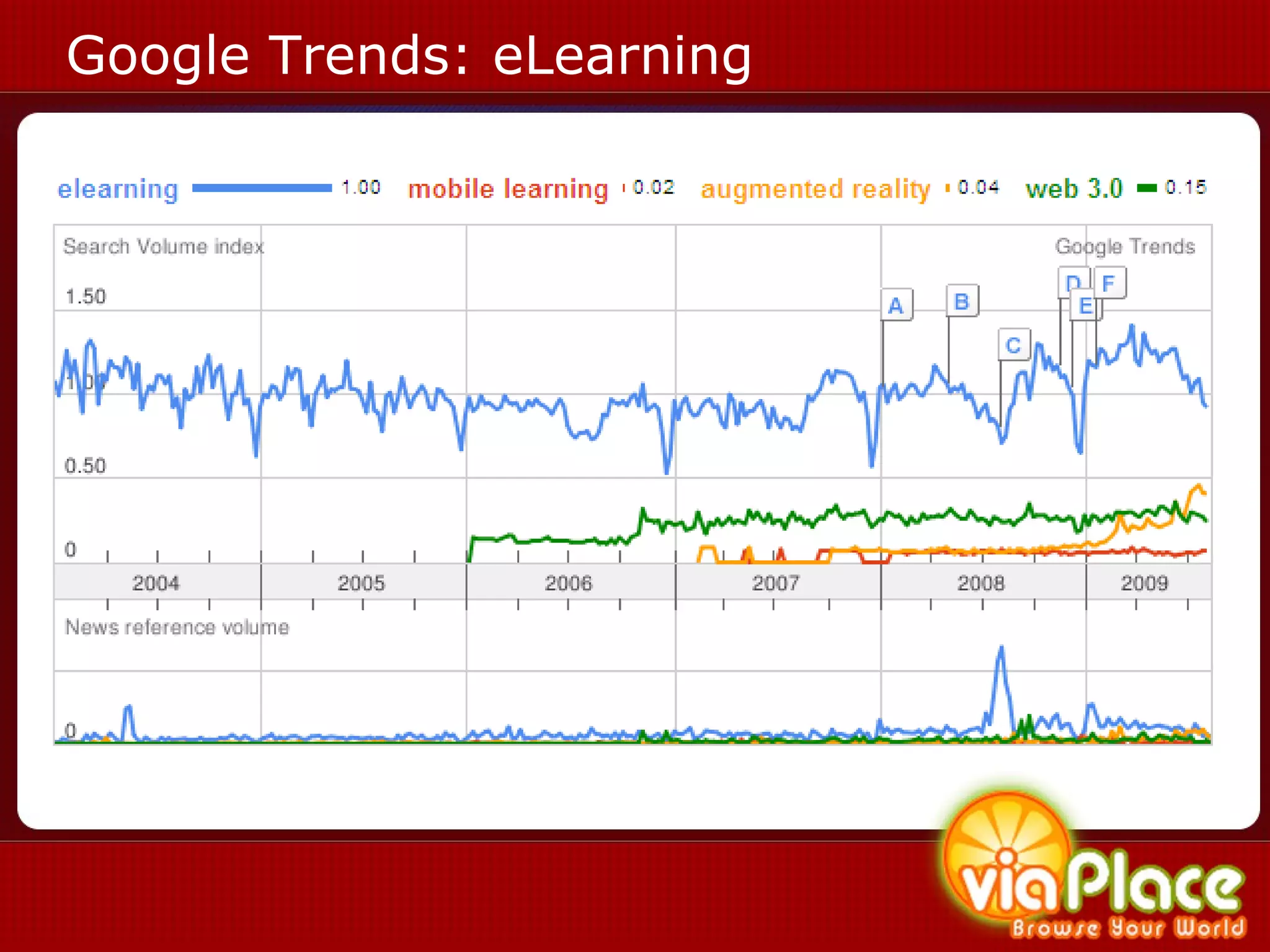
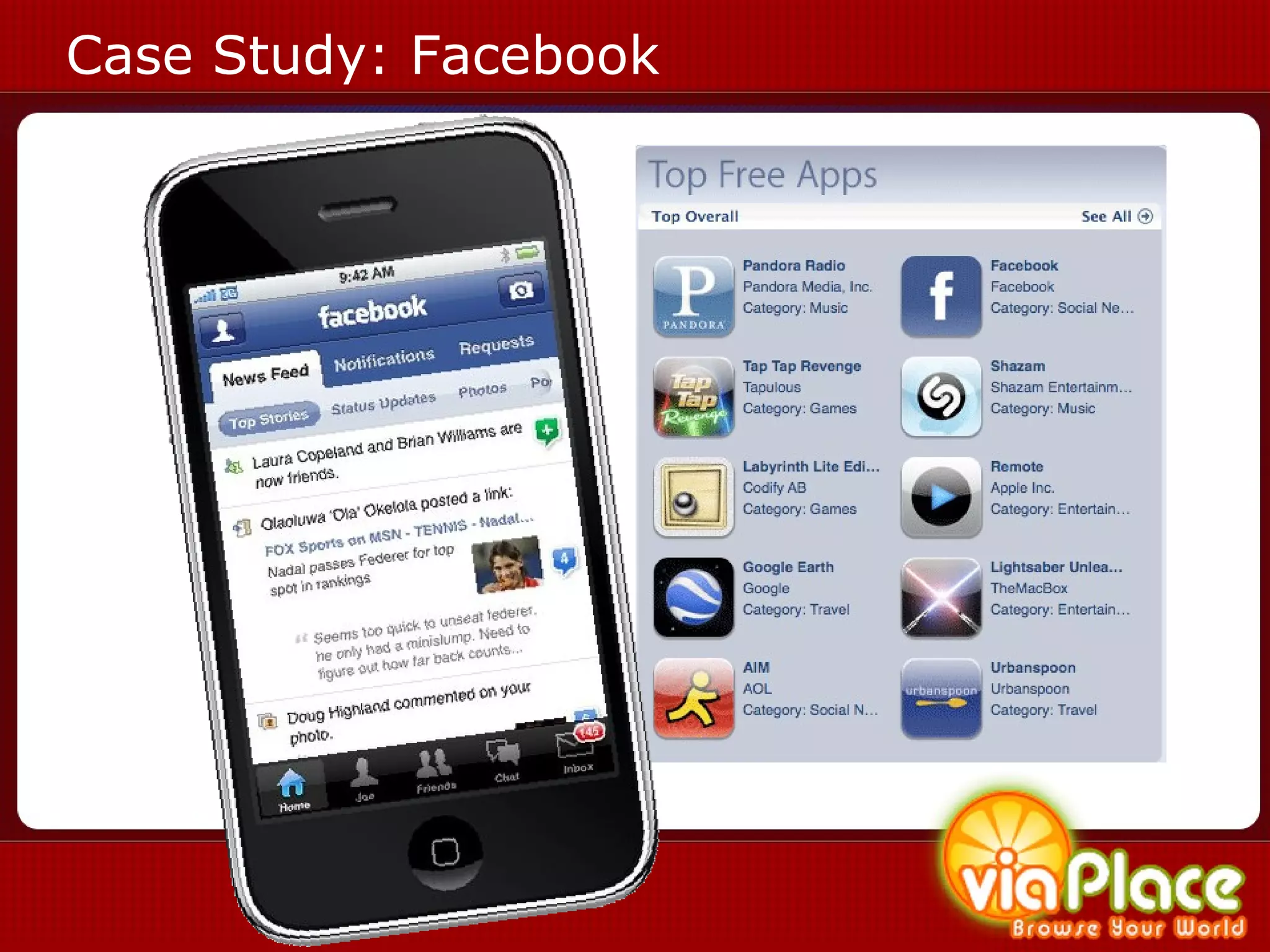
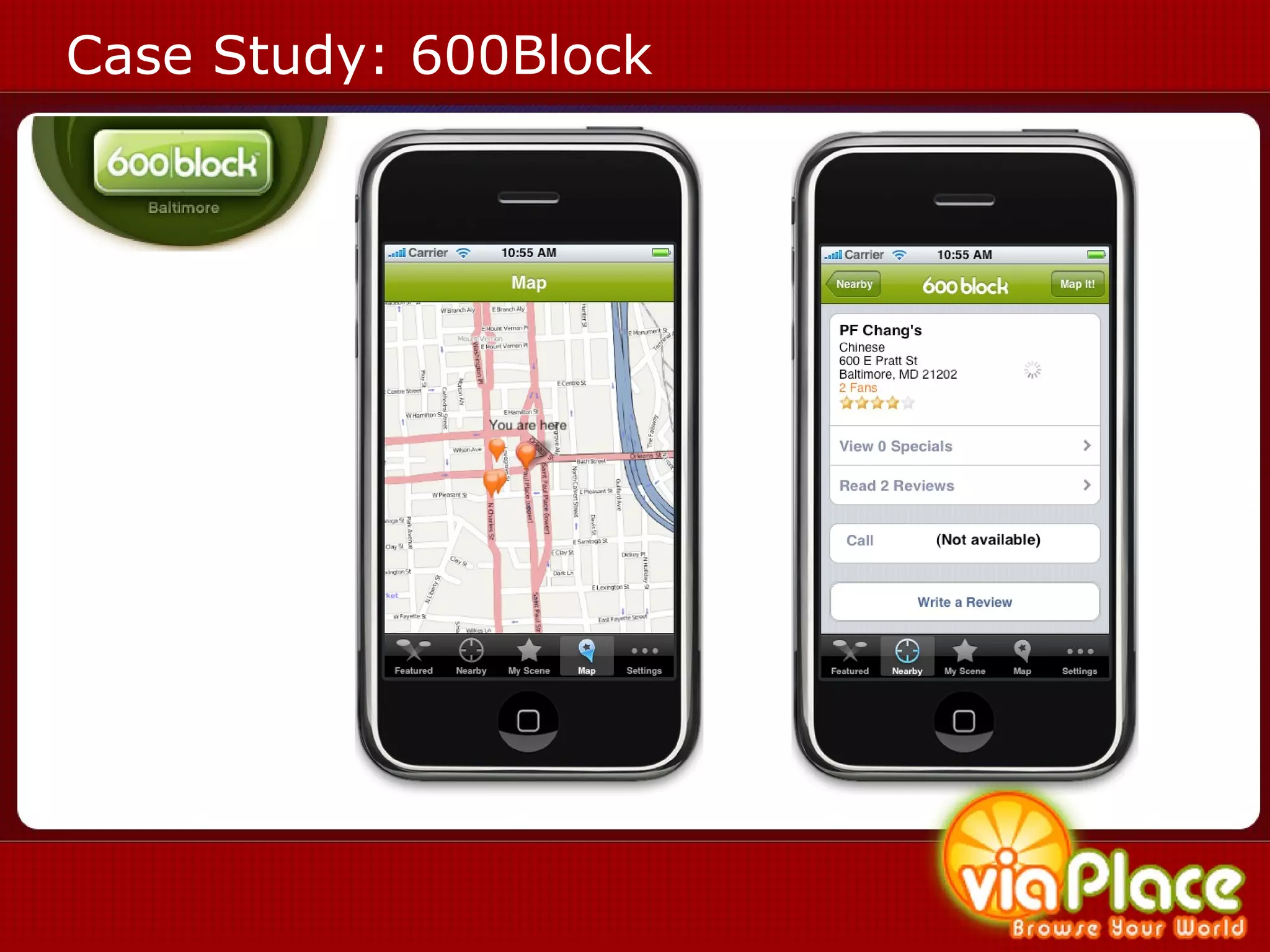
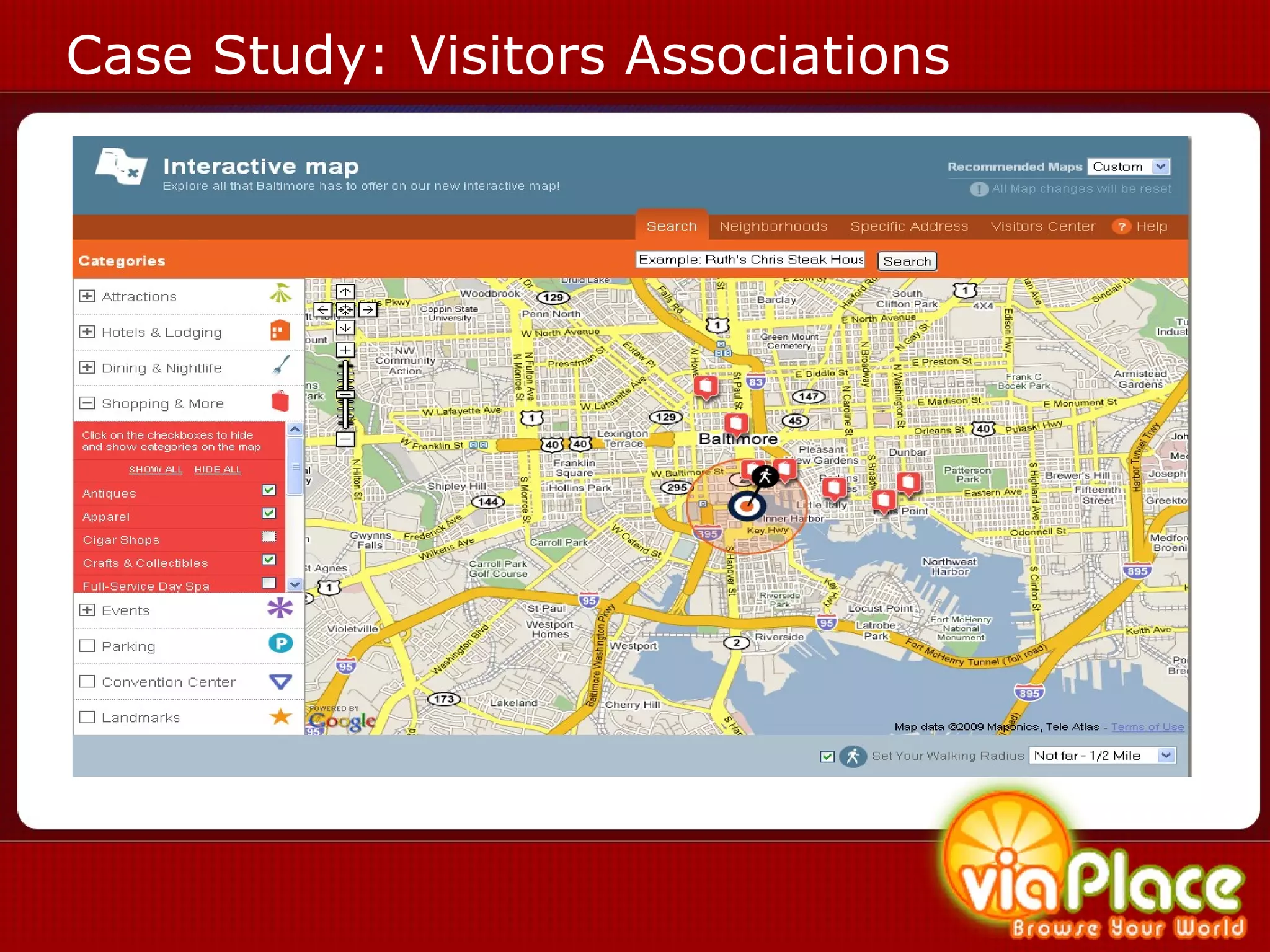
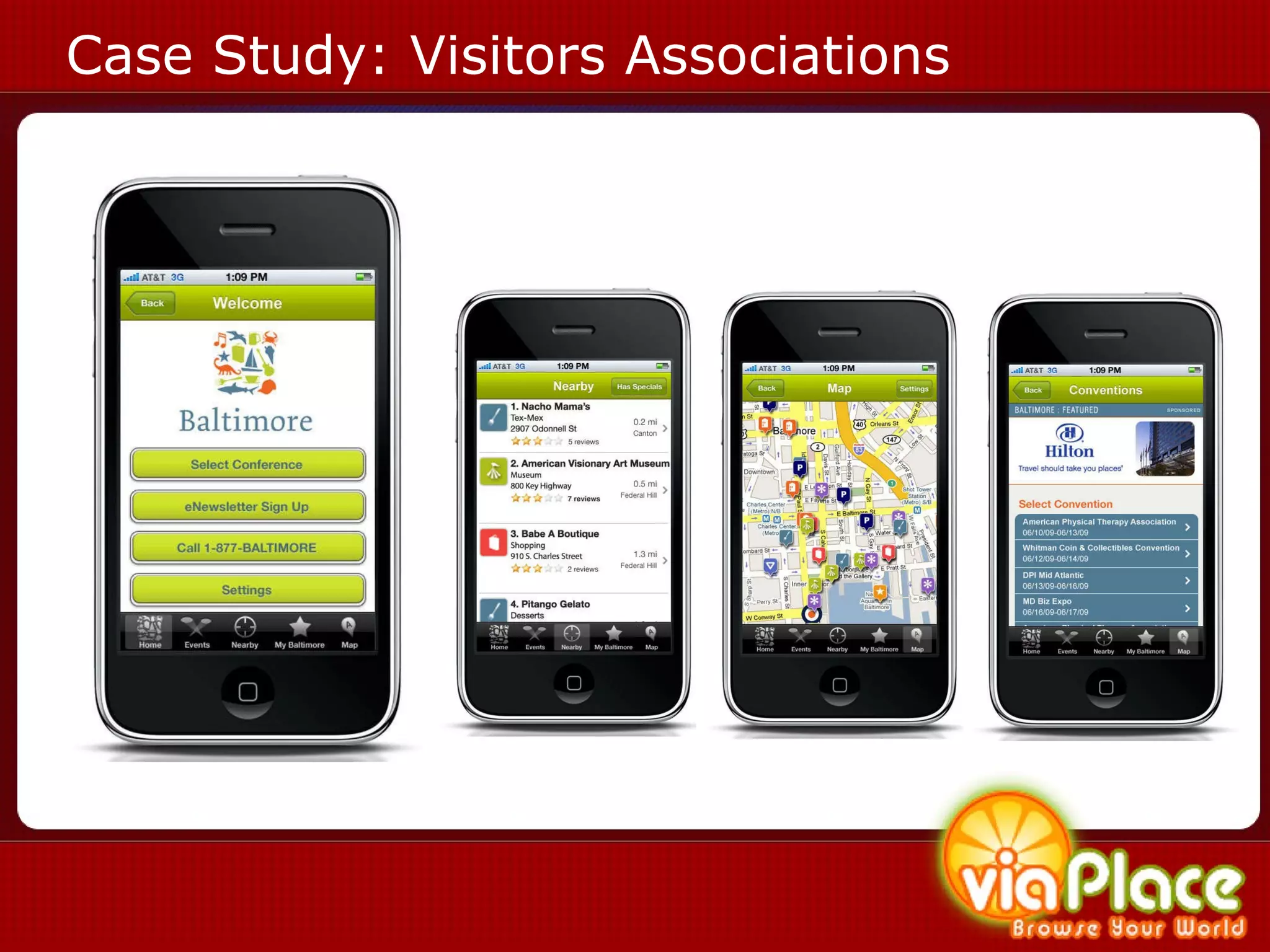
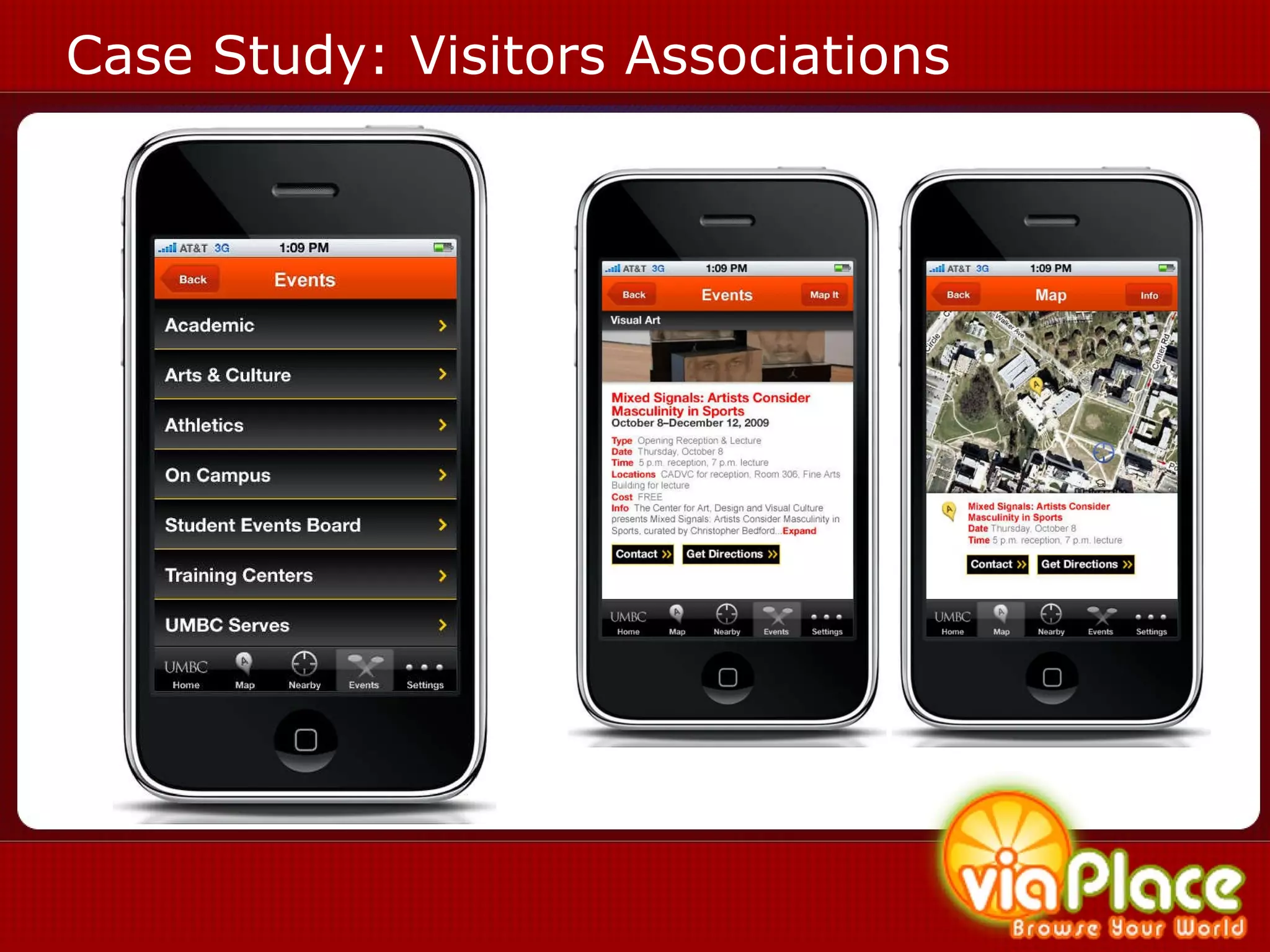
The document discusses the history and evolution of eLearning and mobile learning technologies. It describes how eLearning progressed from early classroom instruction to distance learning and web-based models. More recently, location-based mobile experiences have emerged that provide personalized educational content based on a user's location through their smartphone. Examples like viaPlace are given that use augmented reality to create interactive educational trails at specific locations. Barriers to the growth of these technologies are also mentioned.
![viaPlace – Location Based mobile Learning Todd Marks President & CEO Mindgrub Technologies LLC [email_address] tmarks@umbc.edu](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/viaplacesalt-090828115458-phpapp02/75/viaPlace-A-Framework-to-Provide-Location-based-Services-Experiences-1-2048.jpg)









































![Questions? (www.mindgrub.com/SALT) Todd Marks President & CEO Mindgrub Technologies LLC [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/viaplacesalt-090828115458-phpapp02/75/viaPlace-A-Framework-to-Provide-Location-based-Services-Experiences-57-2048.jpg)