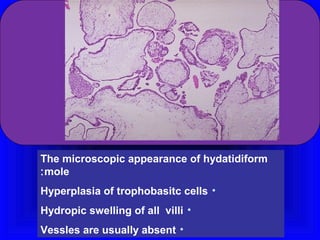
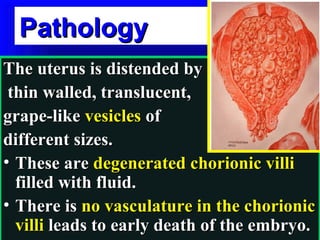
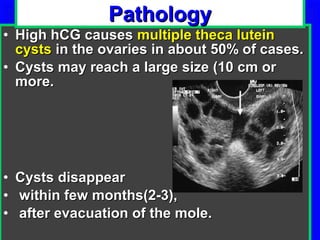
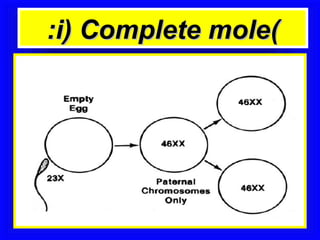
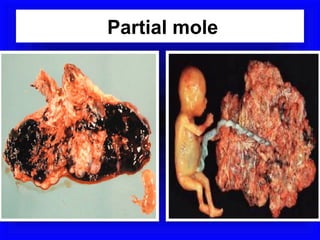
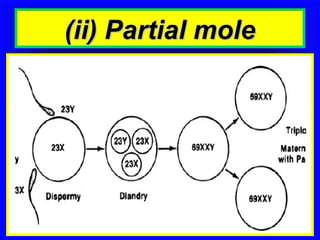
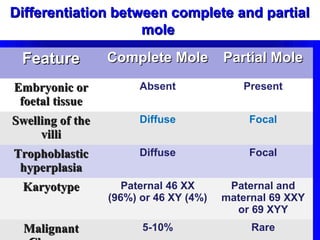
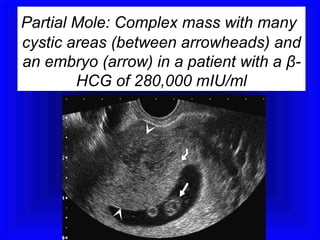
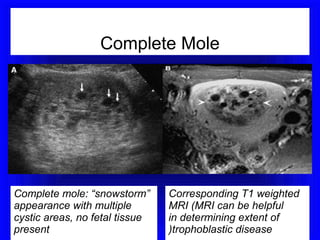
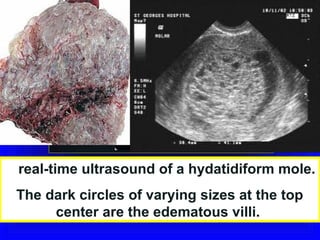
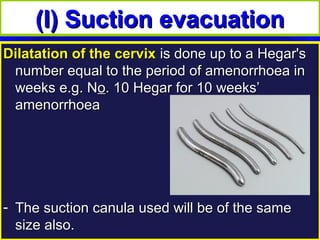
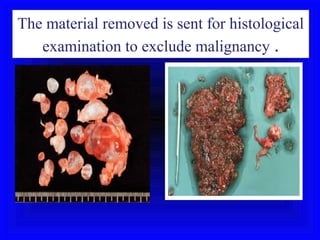
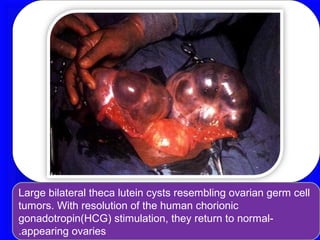
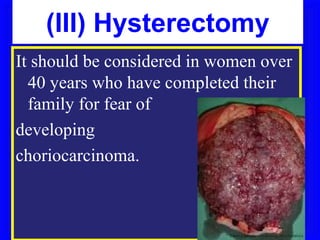
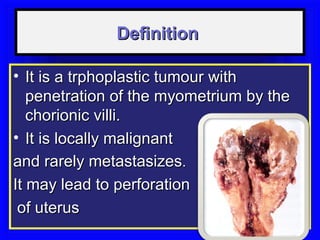
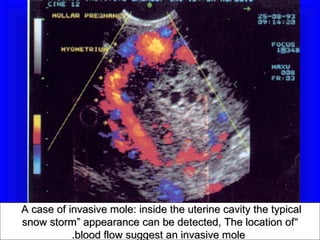
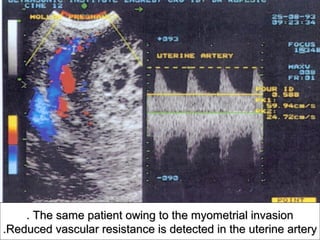
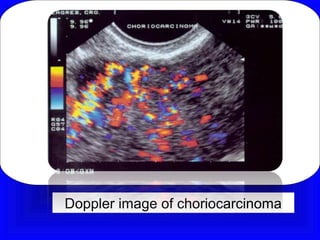
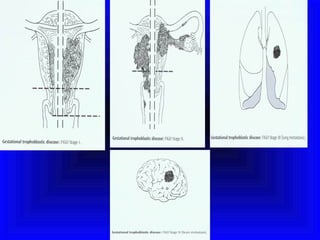
Gestational trophoblastic disease encompasses neoplasms resulting from abnormal trophoblastic proliferation, with hydatidiform moles (complete and partial), invasive moles, and choriocarcinoma as major classifications. Complete moles are characterized by the absence of embryos and result from fertilization of an enucleated ovum, while partial moles contain some embryonic tissue. Diagnosis involves symptoms like exaggerated pregnancy signs and vaginal bleeding, and treatment usually requires surgical evacuation to prevent complications and monitor for potential malignancies.