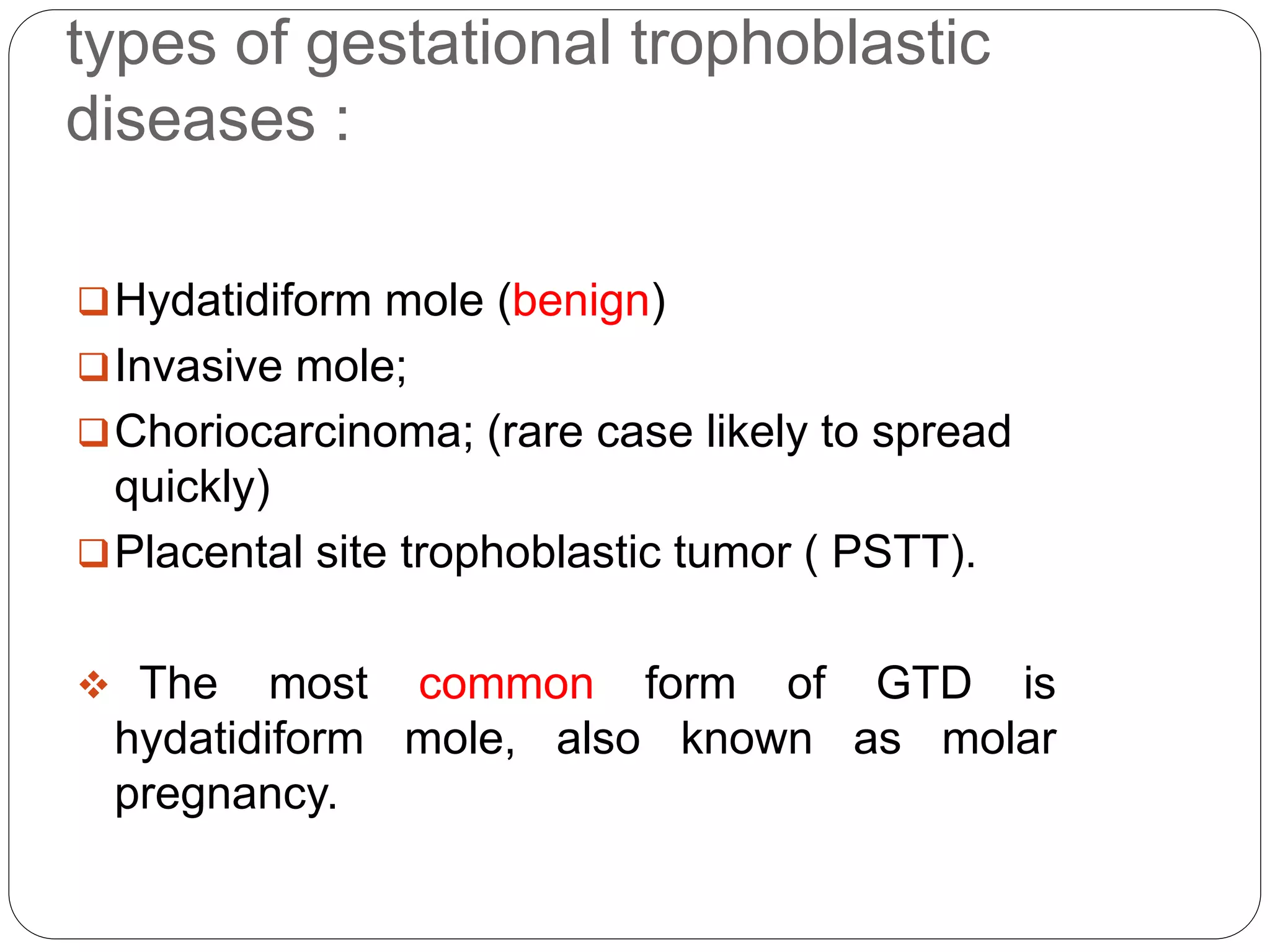
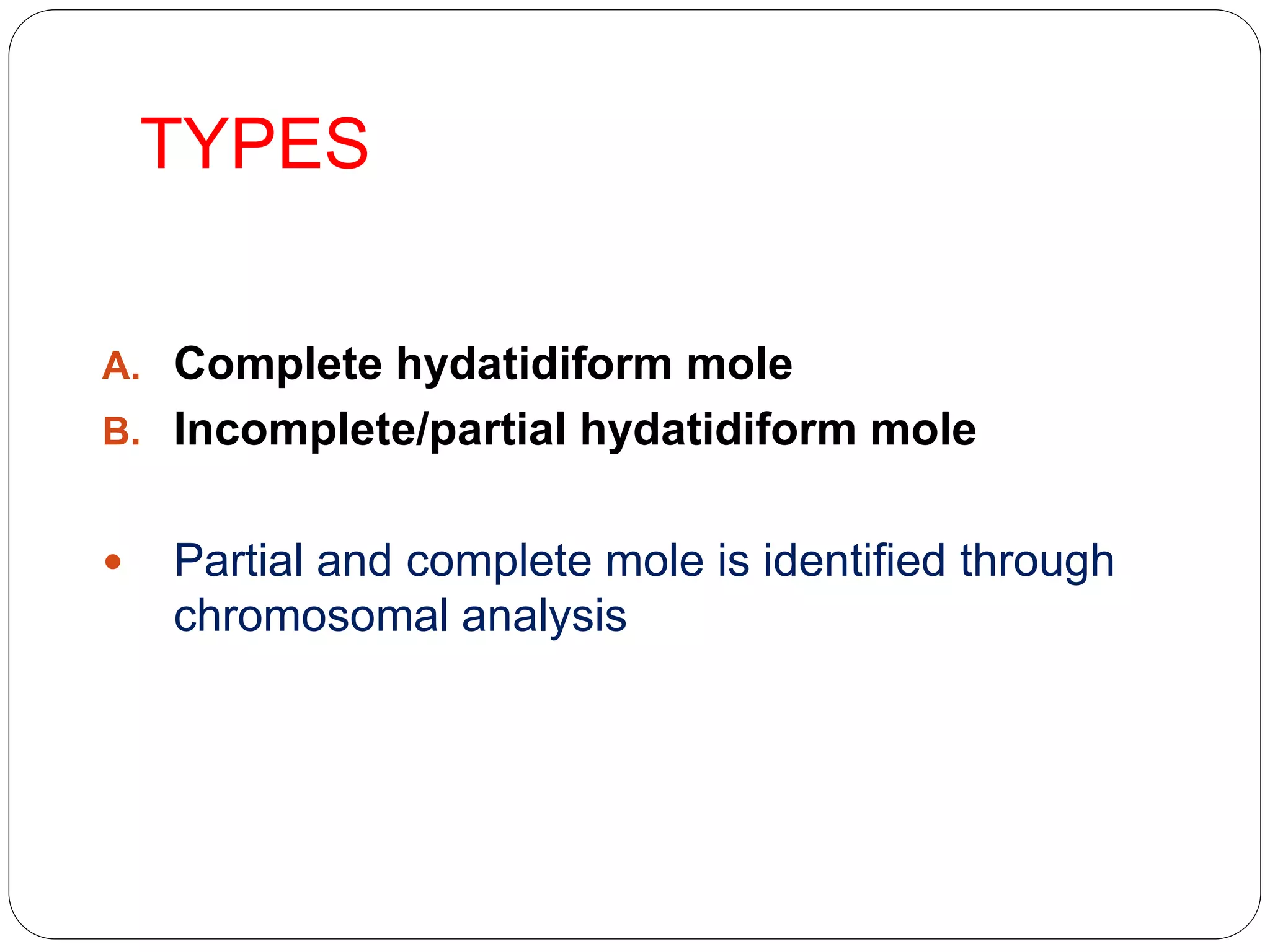
Gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD) includes a spectrum of abnormal pregnancies associated with trophoblastic proliferation. The most common form is a hydatidiform mole, which occurs when a fertilized egg implants abnormally in the uterus. Complete moles have only paternal chromosomes, while partial moles have both maternal and paternal chromosomes. Symptoms include vaginal bleeding, abdominal pain, and high hCG levels. Treatment involves uterine evacuation followed by chemotherapy for high-risk cases to prevent malignant changes. Long-term monitoring of hCG levels is needed due to the risk of persistent trophoblastic disease.