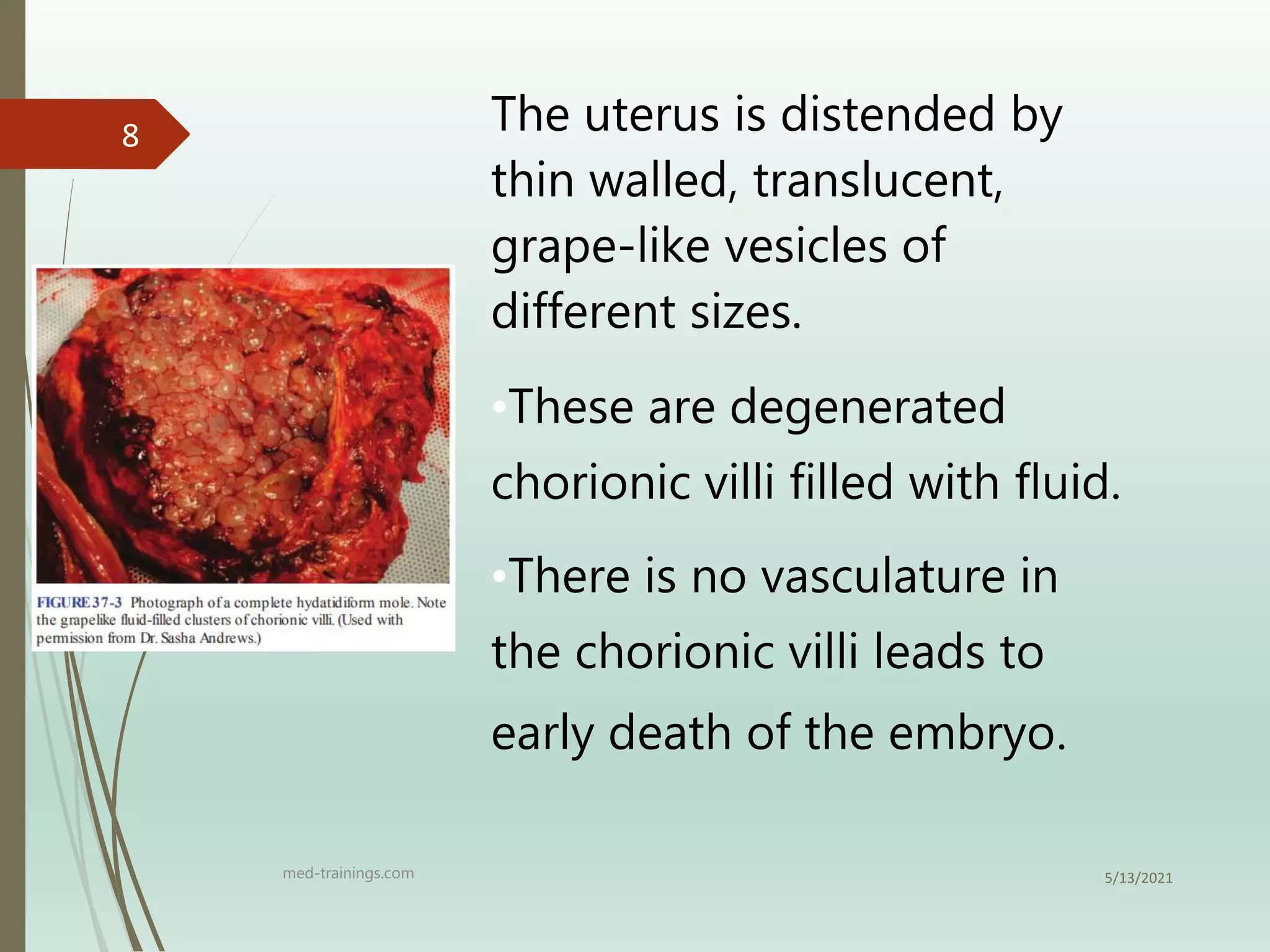
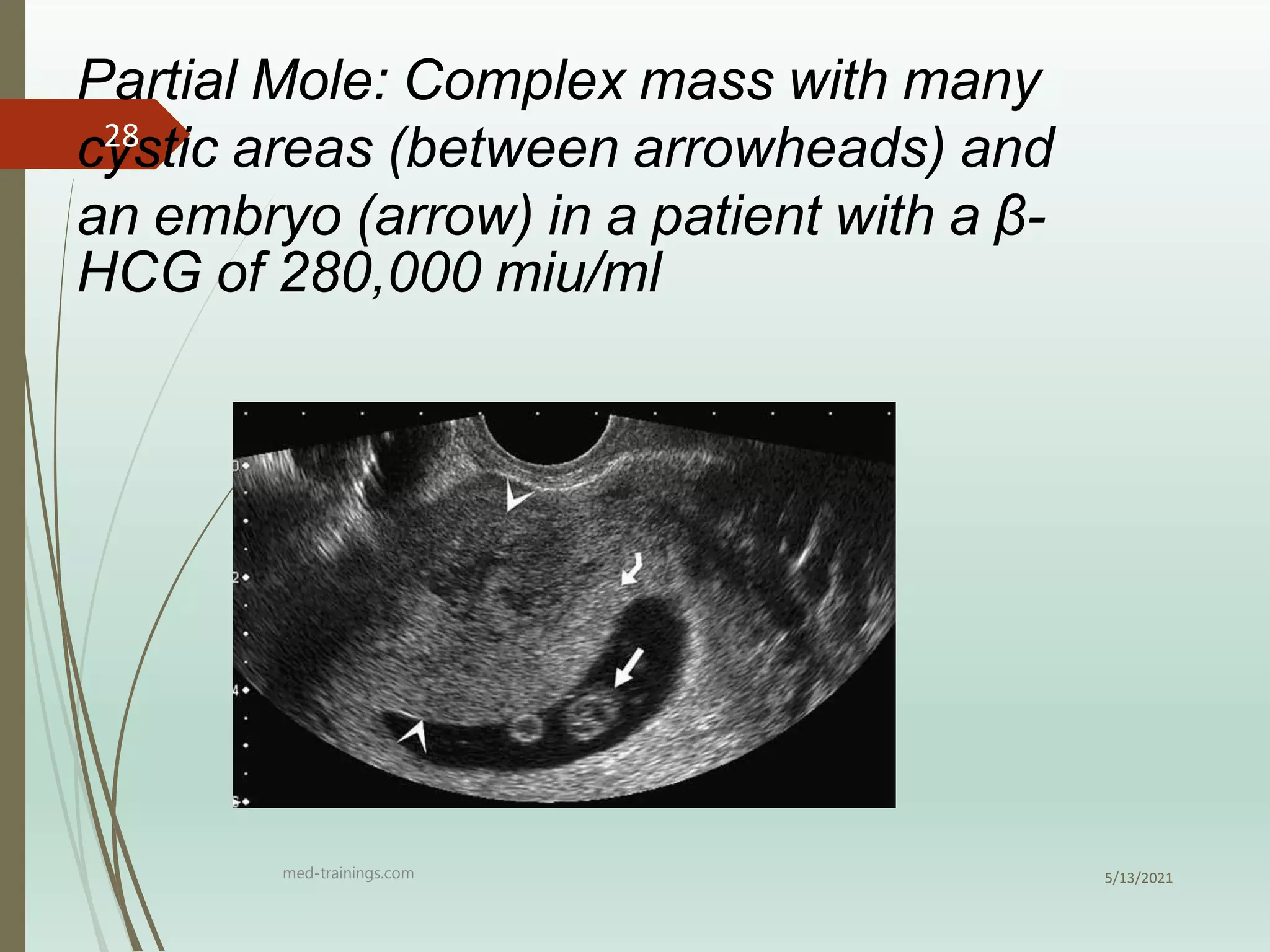
1) Hydatidiform (Vesicular) Mole is a benign neoplasm of the chorionic villi that is characterized by trophoblastic proliferation.
2) It is diagnosed through elevated hCG levels, ultrasound showing the characteristic "snowstorm" appearance, and histological examination of tissue.
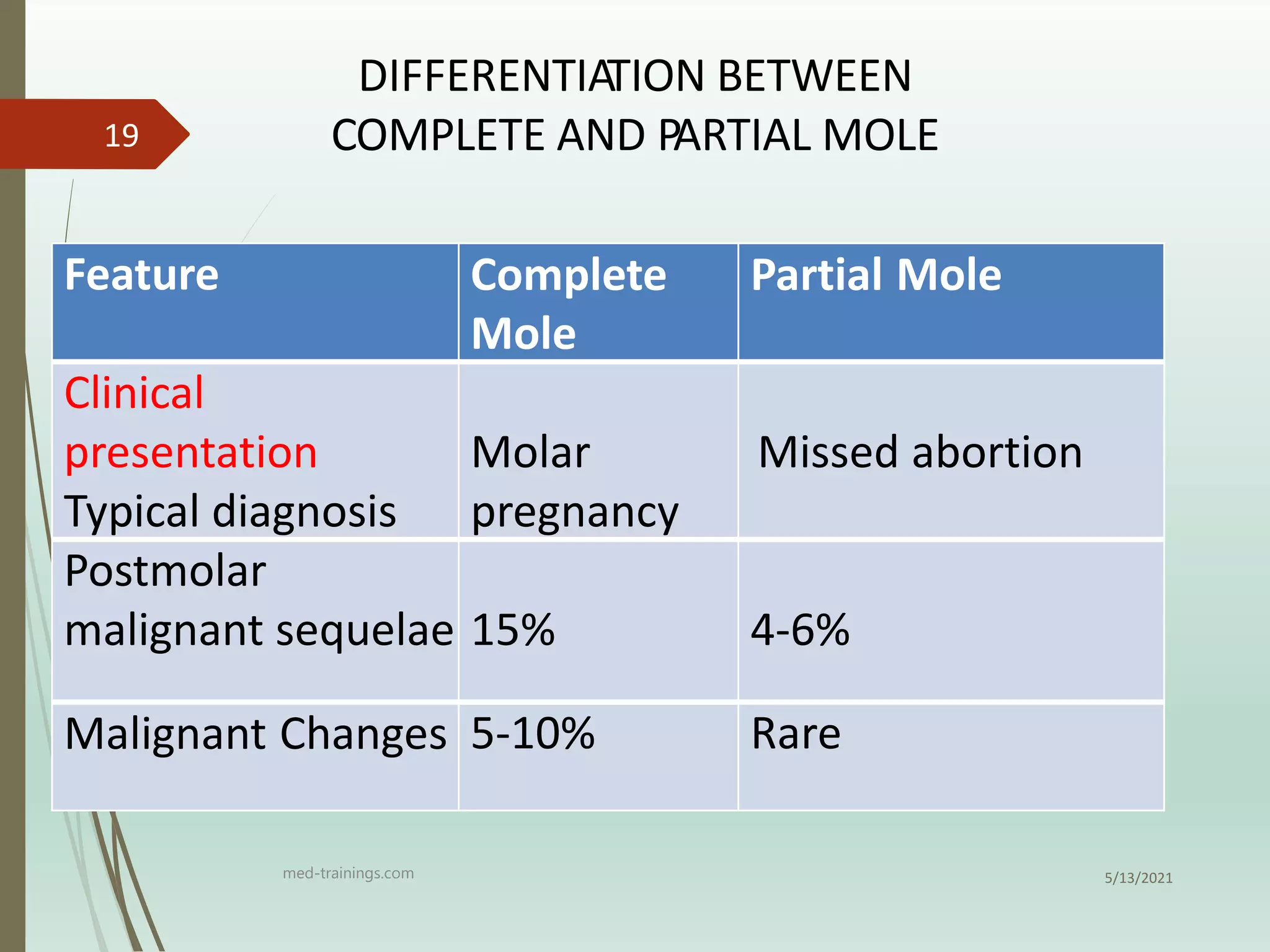
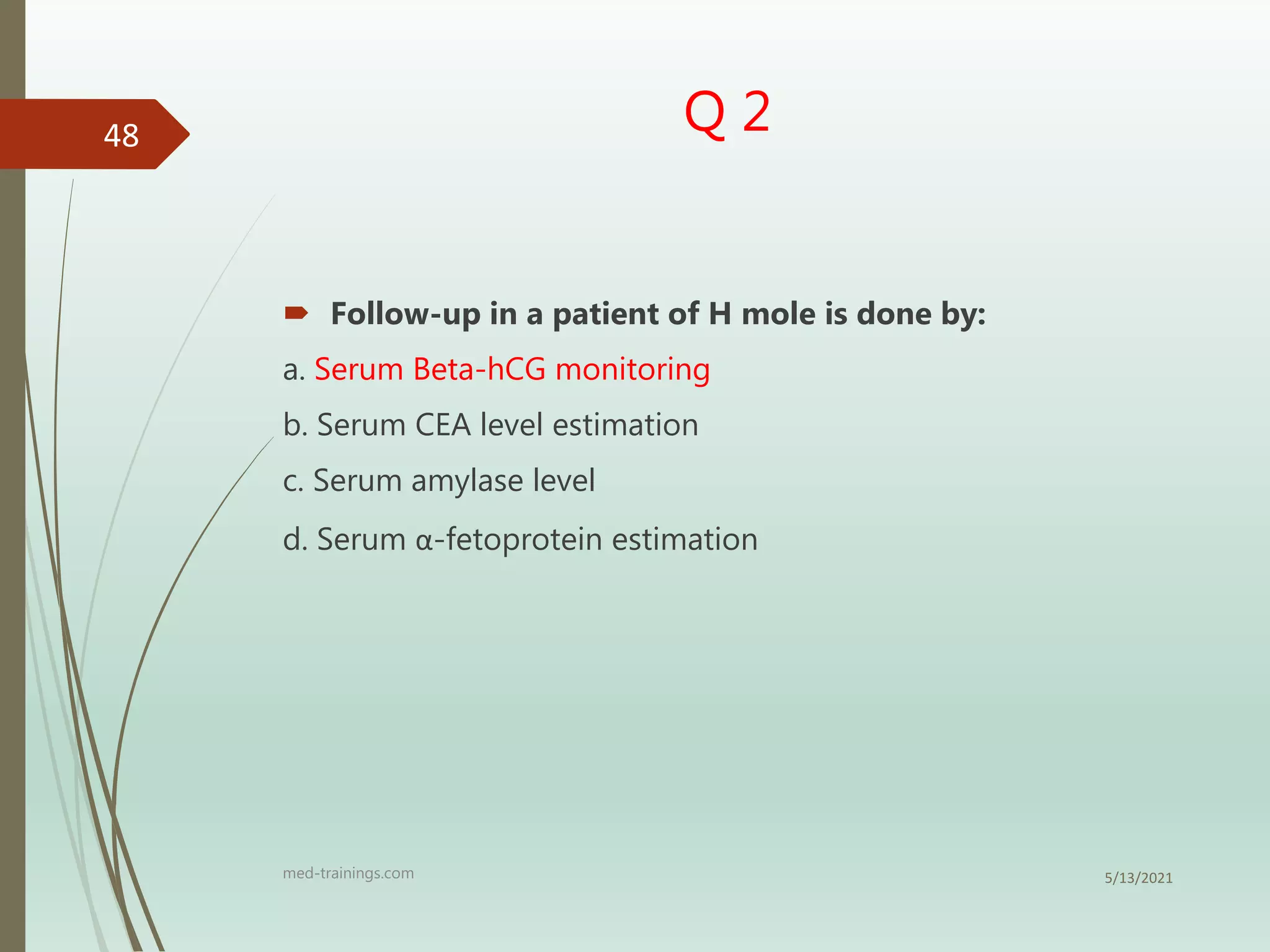
3) Follow up of patients involves regular monitoring of hCG levels to check for resolution or development of gestational trophoblastic neoplasia, as molar pregnancies have a risk of developing into choriocarcinoma or invasive mole.