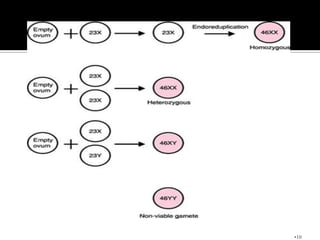
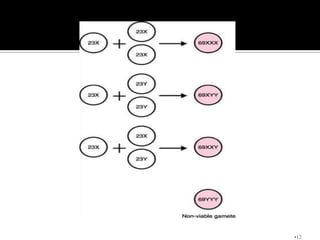
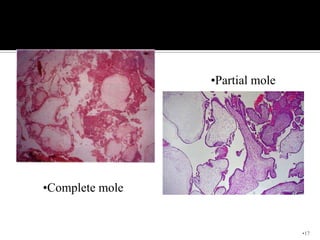
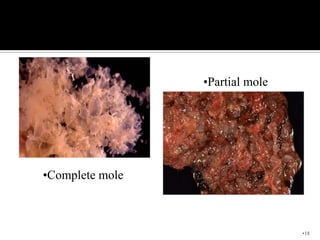
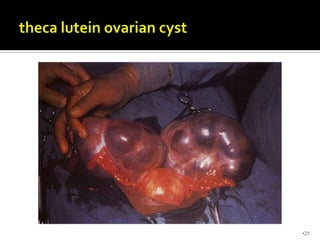
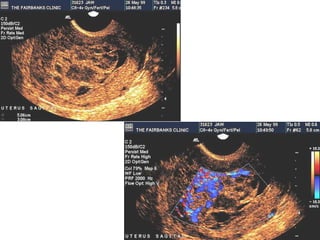
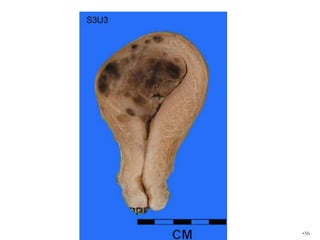
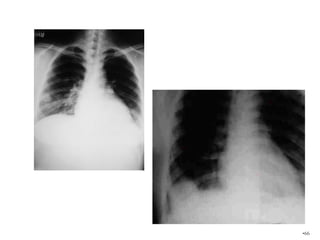
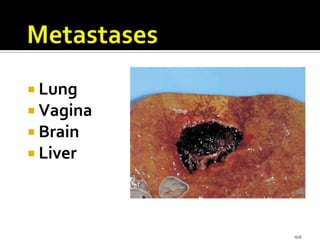
This document defines and classifies gestational trophoblastic disease, which includes hydatidiform mole, invasive mole, and choriocarcinoma. It notes that complete moles have exclusively paternal chromosomes while partial moles are triploid. Suction curettage is usually used to evacuate the uterus for treatment. Patients must be closely monitored with serum hCG tests to check for persistent trophoblastic tissue, which may develop into invasive mole or choriocarcinoma in about 10% of cases. Chemotherapy is used if hCG levels remain elevated or metastases are present.