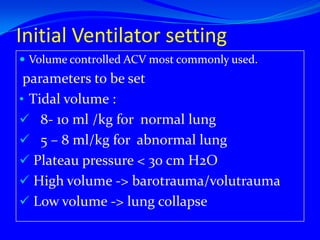
This document provides information on the management of patients on mechanical ventilation. It discusses the indications for mechanical ventilation including inadequate oxygenation and ventilation. It then covers the mechanisms of oxygen transport and various causes of inadequate oxygenation and perfusion. The document outlines the purposes of ventilation and procedures for initiation and settings of mechanical ventilation including modes, parameters, and monitoring of patients. It discusses potential problems during ventilation and goals of ventilation. Finally, the document reviews weaning from mechanical ventilation.