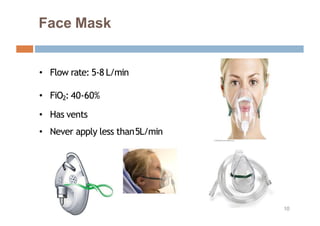
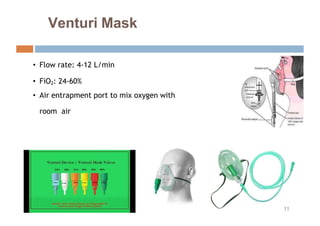
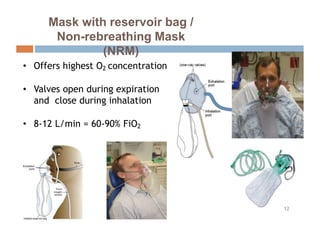
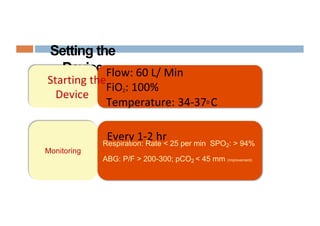
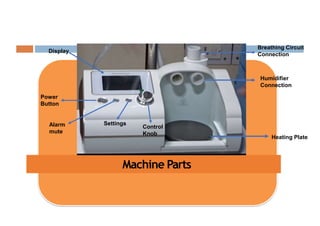
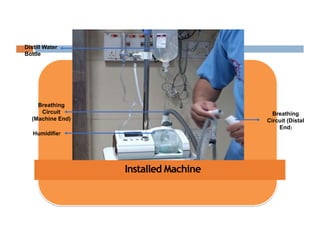
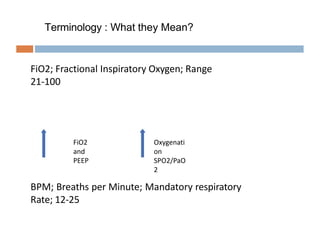
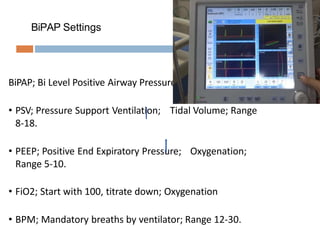
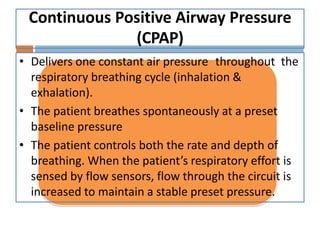
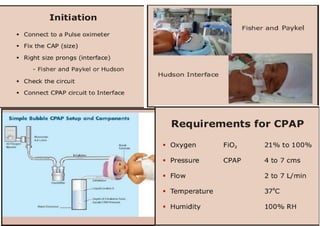
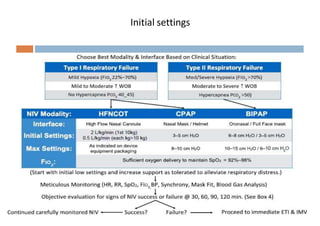
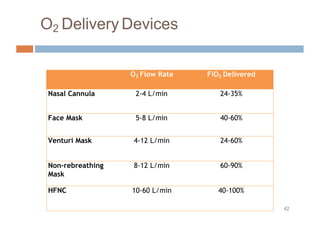
Oxygen therapy and non-invasive ventilation (NIV) such as BiPAP and CPAP can effectively treat hypoxemia. The appropriate use of oxygen delivery devices and settings is important to correct hypoxemia while avoiding overuse and potential harm. Key devices include nasal prongs, masks, high flow nasal cannula (HFNC), and NIV. Settings for NIV include pressures, PEEP, respiratory rate, and FiO2. Proper application and monitoring of devices is needed to safely deliver therapy and escalate or de-escalate support based on patient response and oxygenation levels.