1) Respiratory failure is defined as failure of oxygenation or carbon dioxide elimination and can be acute or chronic. It is classified as type 1 (hypoxemic) or type 2 (hypercapnic).
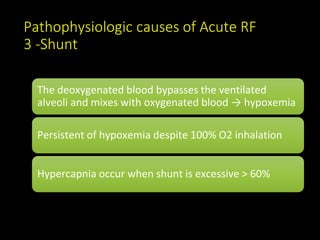
2) Causes of acute respiratory failure include hypoventilation, V/Q mismatching, intrapulmonary shunting, and diffusion abnormalities. Common causes are pneumonia, pulmonary edema, and ARDS.
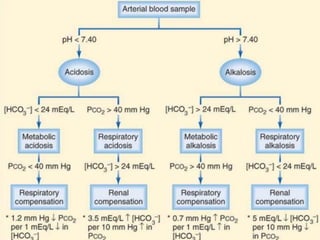
3) Diagnosis involves clinical presentation, blood gas analysis, chest imaging, and pulmonary function tests. Management focuses on airway support, oxygen therapy, mechanical ventilation, and treating the underlying cause.