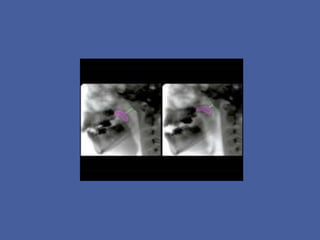
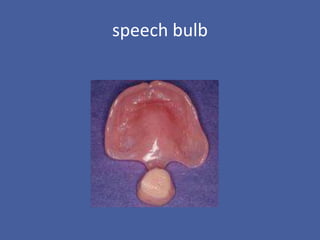
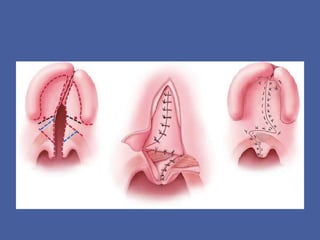
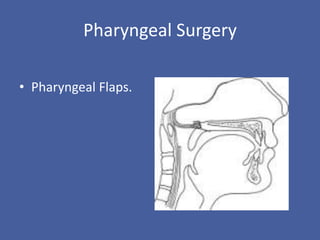
Velopharyngeal insufficiency (VPI) is the inability to achieve closure of the velopharyngeal port during speech, commonly caused by cleft palate or other structural abnormalities. Signs include hypernasality, nasal emission, and imprecise consonant production. Treatment options include speech therapy, prosthetics like palatal lifts, and surgery like pharyngeal flaps or sphincter pharyngoplasty to improve closure of the airway during speech. Surgical complications can include bleeding, airway obstruction, or sleep apnea requiring revision in some cases.