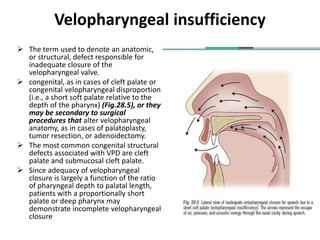
This document discusses velopharyngeal dysfunction (VPD), which refers to impaired functioning of the velopharyngeal valve that separates the oral and nasal cavities during speech. There are several types of VPD, including velopharyngeal insufficiency due to anatomical defects like cleft palate, velopharyngeal incompetence due to neurological issues, and velopharyngeal mislearning where the mechanism is capable of closure but sounds are mislearned. Diagnosis requires assessing the patient's speech and velopharyngeal anatomy and function. Treatment may involve speech therapy or surgery to repair anatomical defects or restore competence. Successful management requires a collaborative team approach between surgeons and speech therapists.