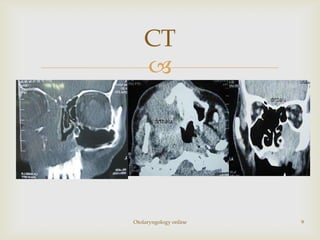
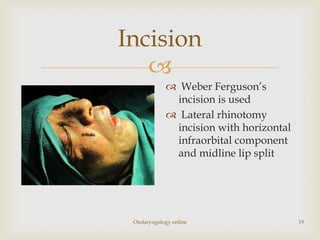
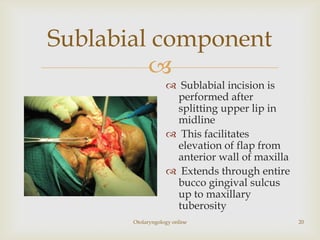
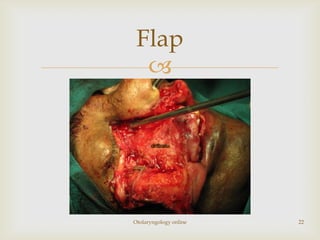
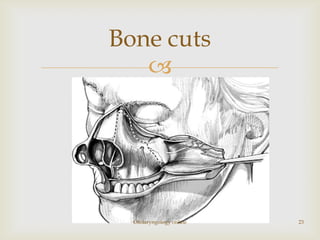
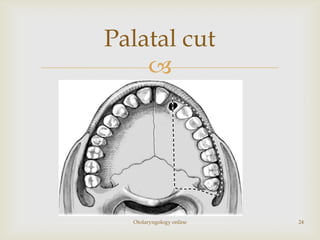
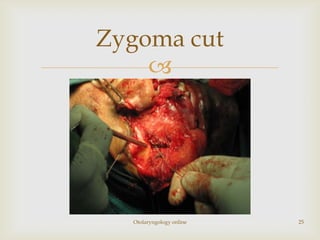
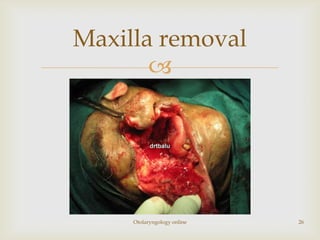
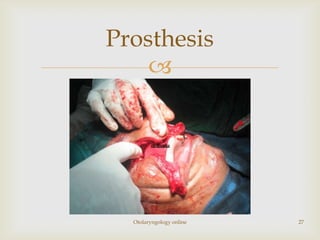
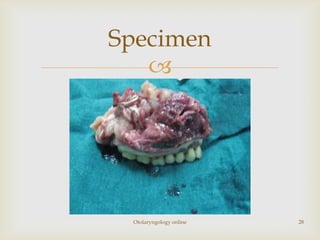
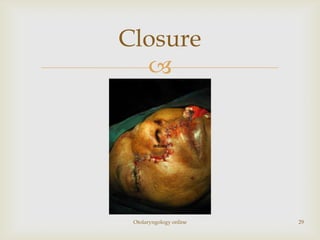
Total maxillectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the entire maxilla bone. It was first described in the 1820s and approaches have been refined over time. It is indicated for malignant tumors involving the maxilla, extensive benign tumors, or fungal/granulomatous infections. Contraindications include poor general health, bilateral orbital involvement, or skull base extension. Potential complications include bleeding, infection, epiphora, skin graft breakdown, numbness, and atrophic rhinitis. Careful surgical planning and follow up are required due to significant reconstruction and rehabilitation needs.