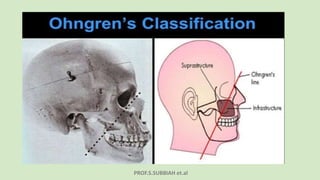
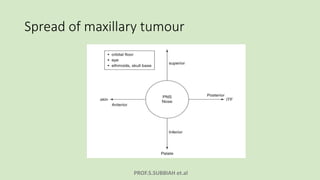
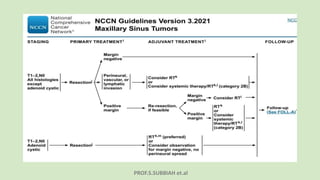
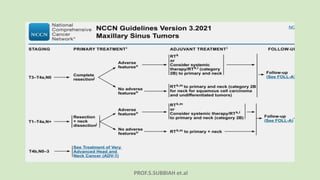
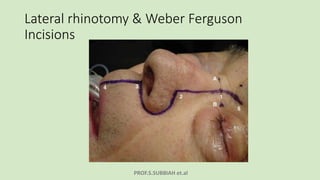
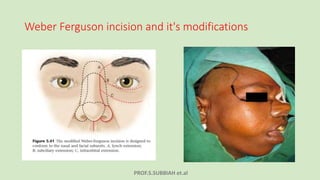
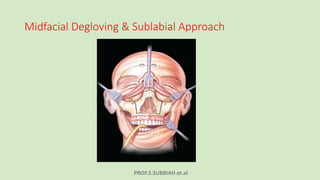
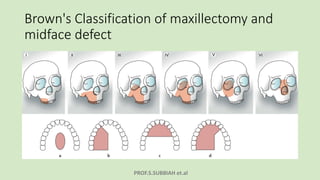
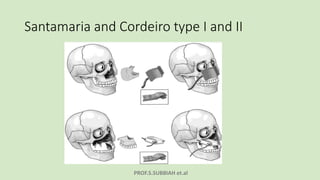
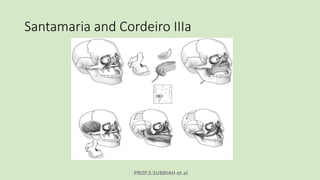
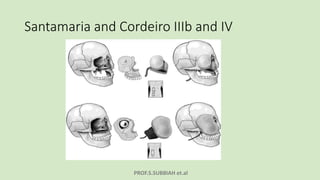
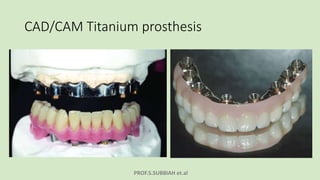
This document discusses maxillectomy, which is the surgical removal of part or all of the maxilla bone. It provides a history of maxillectomy and describes the anatomy of the maxilla bone. It also discusses different classifications of maxillectomy procedures based on the extent of bone removed. The common indications for maxillectomy are malignant tumors like squamous cell carcinoma. The approaches used include lateral rhinotomy, Weber-Ferguson, and transoral-transpalatal. Reconstruction options involve dental prosthetics, maxillofacial prosthetics, and titanium implants.