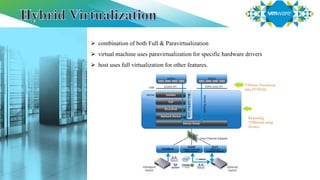
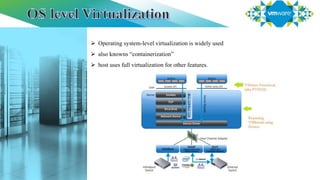
Virtualization refers to creating virtual versions of hardware and resources rather than actual physical versions. There are several types of virtualization including server, storage, desktop, application, and network virtualization. Server virtualization partitions physical servers into smaller virtual servers to maximize resource use. There are two main approaches to full virtualization: software-assisted which uses binary translation, and hardware-assisted which uses virtualization technology in Intel/AMD CPUs. Paravirtualization modifies guest operating systems to communicate directly with the hypervisor rather than simulating hardware. Hybrid virtualization uses paravirtualization for drivers and full virtualization for other features.