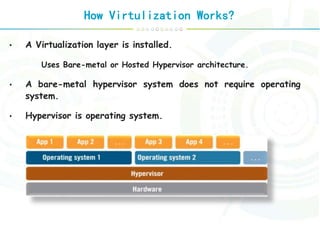
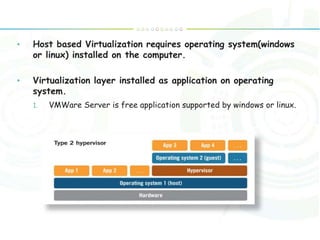
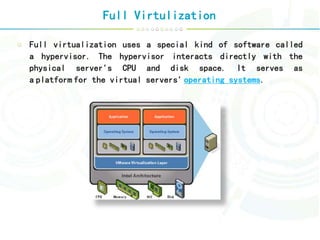
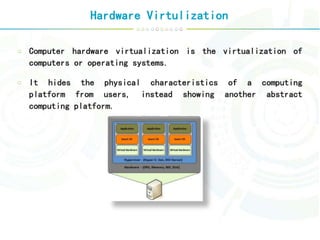
Virtualization is a technology that abstracts computer resources by transforming hardware into software. It allows multiple operating systems to run simultaneously on a single computer as virtual machines. There are different types of virtualization including full virtualization, paravirtualization, and hardware-assisted virtualization. Virtualization enables key aspects of cloud computing like scalability, availability, manageability, and performance by pooling and abstracting hardware resources and allowing virtual machines to be easily provisioned, migrated, and scaled.