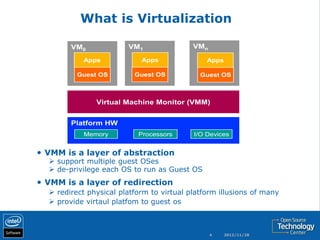
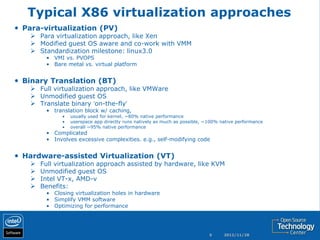
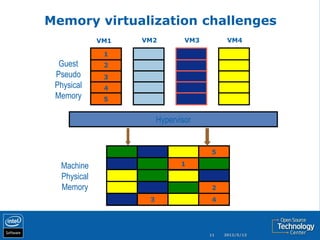
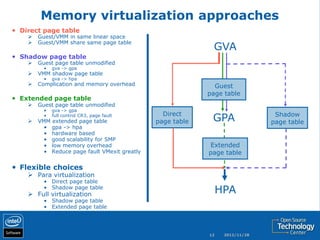
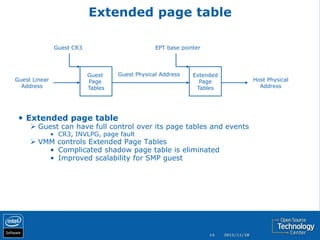
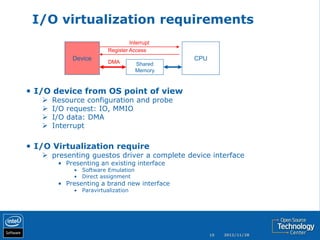
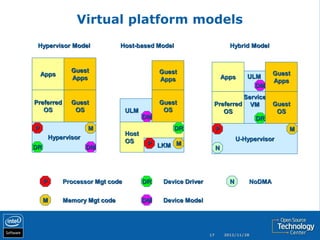
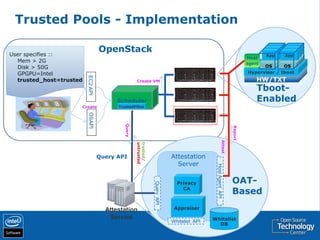
The document discusses the history and usage of virtualization technology, provides an overview of CPU, memory, and I/O virtualization, compares the Xen and KVM virtualization architectures, and describes some Intel work to support virtualization in OpenStack including the Open Attestation service.