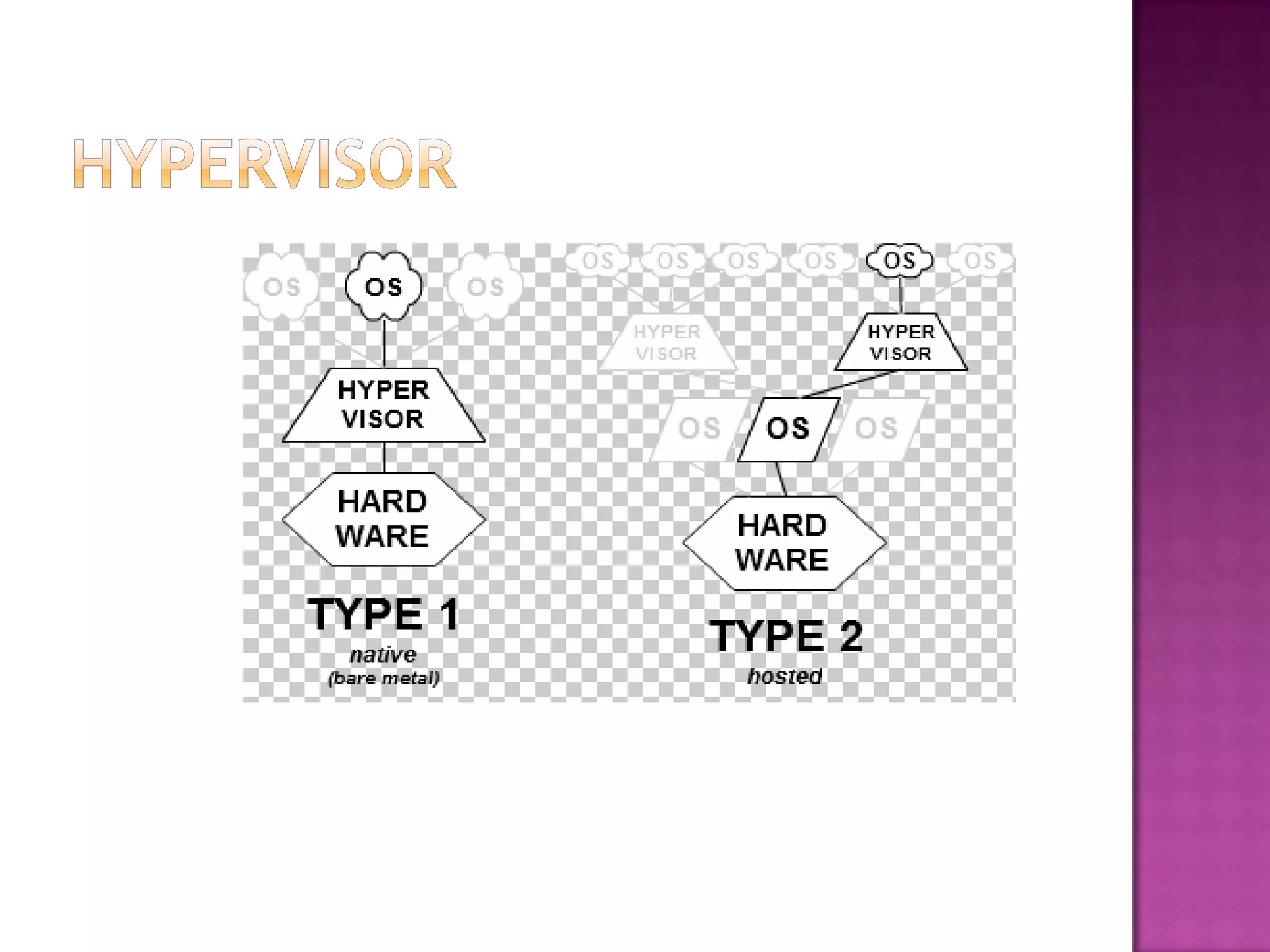
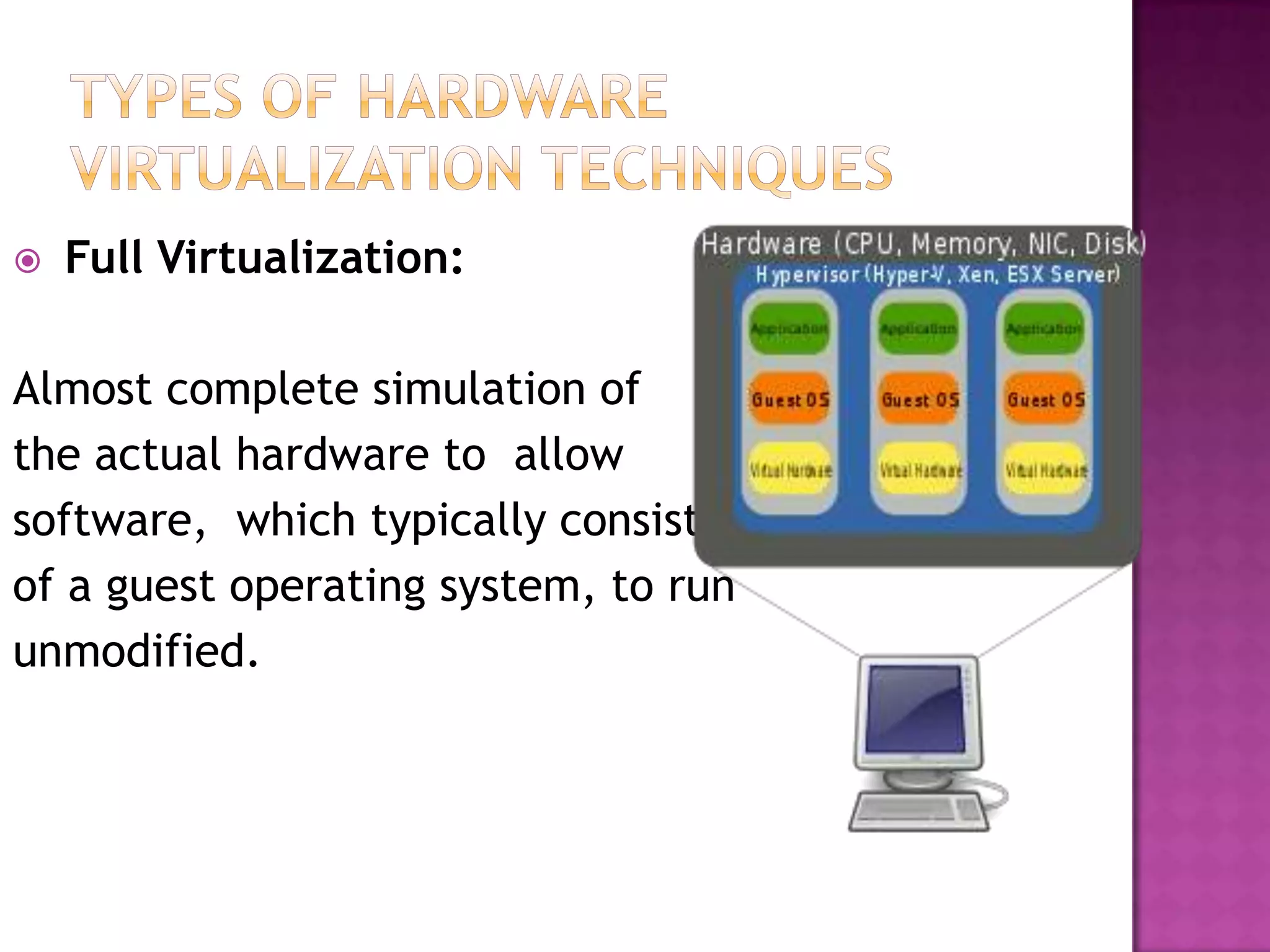
Hardware virtualization allows multiple operating systems to run on a single machine using a virtual machine manager (VMM) or hypervisor. The hypervisor creates virtual machines as guest machines that run on the host hardware. Full virtualization completely simulates the hardware, allowing unmodified guest operating systems. Partial virtualization simulates some but not all of the target environment, requiring some guest programs to be modified. Hardware virtualization disaster recovery environments use hardware and software protection based on business continuity needs, including tape backup for long-term data archiving and whole file or application replication to another disk. While virtualization reduces IT infrastructure complexity through better resource utilization, it still requires purchasing and maintaining servers and software.