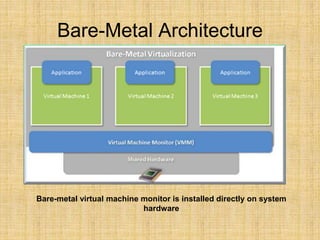
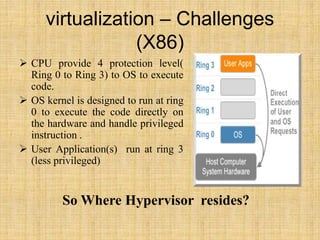
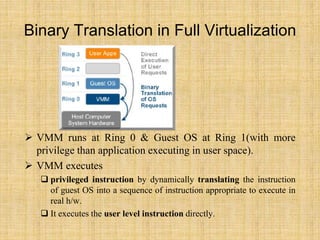
This document discusses full virtualization techniques. It defines full virtualization as simulating hardware to allow any OS to run unmodified in a virtual machine. It describes the challenges of virtualizing the x86 architecture and how binary translation is used to allow guest OSes to run at a higher privilege level. The document outlines hosted and bare-metal virtualization architectures and their pros and cons. It provides examples of using full virtualization for desktop and server virtualization/cloud computing. It also gives steps to implement hosted full virtualization using Oracle VM VirtualBox on Windows 7.