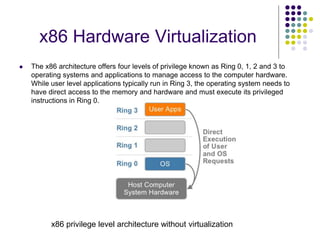
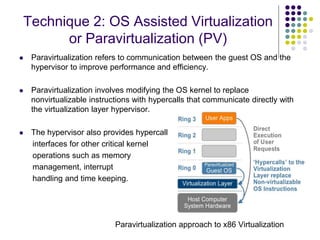
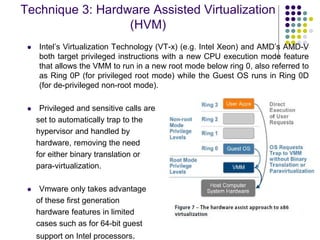
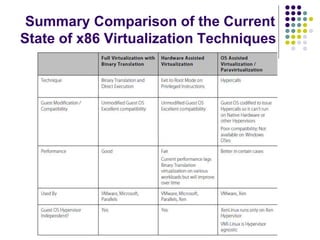
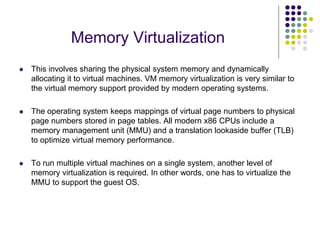
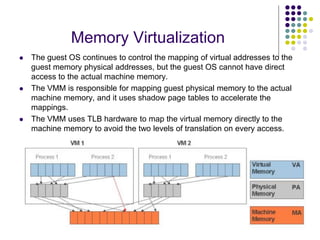
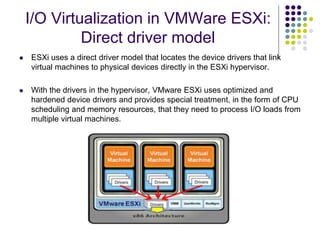
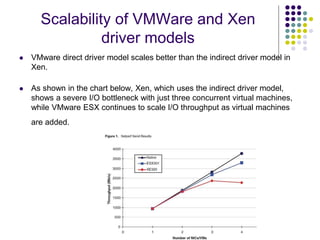
Full virtualization uses binary translation to virtualize privileged instructions without modifying the guest OS, but has performance overhead. Paravirtualization modifies the guest OS kernel to replace privileged calls with hypercalls for better performance. Hardware virtualization extensions in Intel VT-x and AMD-V allow virtualizing privileged instructions in hardware. Memory virtualization uses shadow page tables to map guest physical to host physical memory. I/O virtualization presents virtual devices to VMs and translates requests to physical hardware. VMWare uses optimized direct drivers in ESXi for better I/O scalability compared to Xen's indirect driver model.