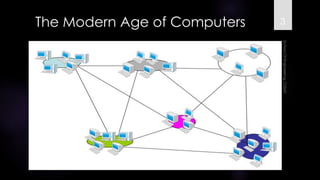
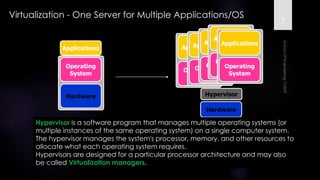
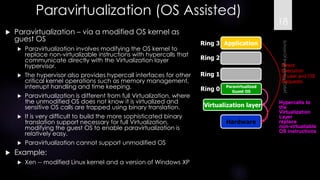
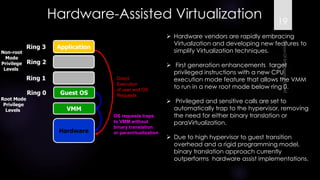
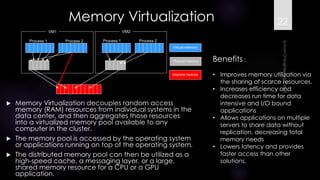
The document discusses virtualization, outlining its definition as the abstraction of computer resources that allows for multiple execution environments. It highlights the benefits of virtualization, such as workload consolidation, resource optimization, and increased security, while also addressing challenges like hardware compatibility and privileged operations. Additionally, various types of virtualization, including full virtualization, paravirtualization, and OS-level virtualization, are examined, along with their respective technologies and applications.