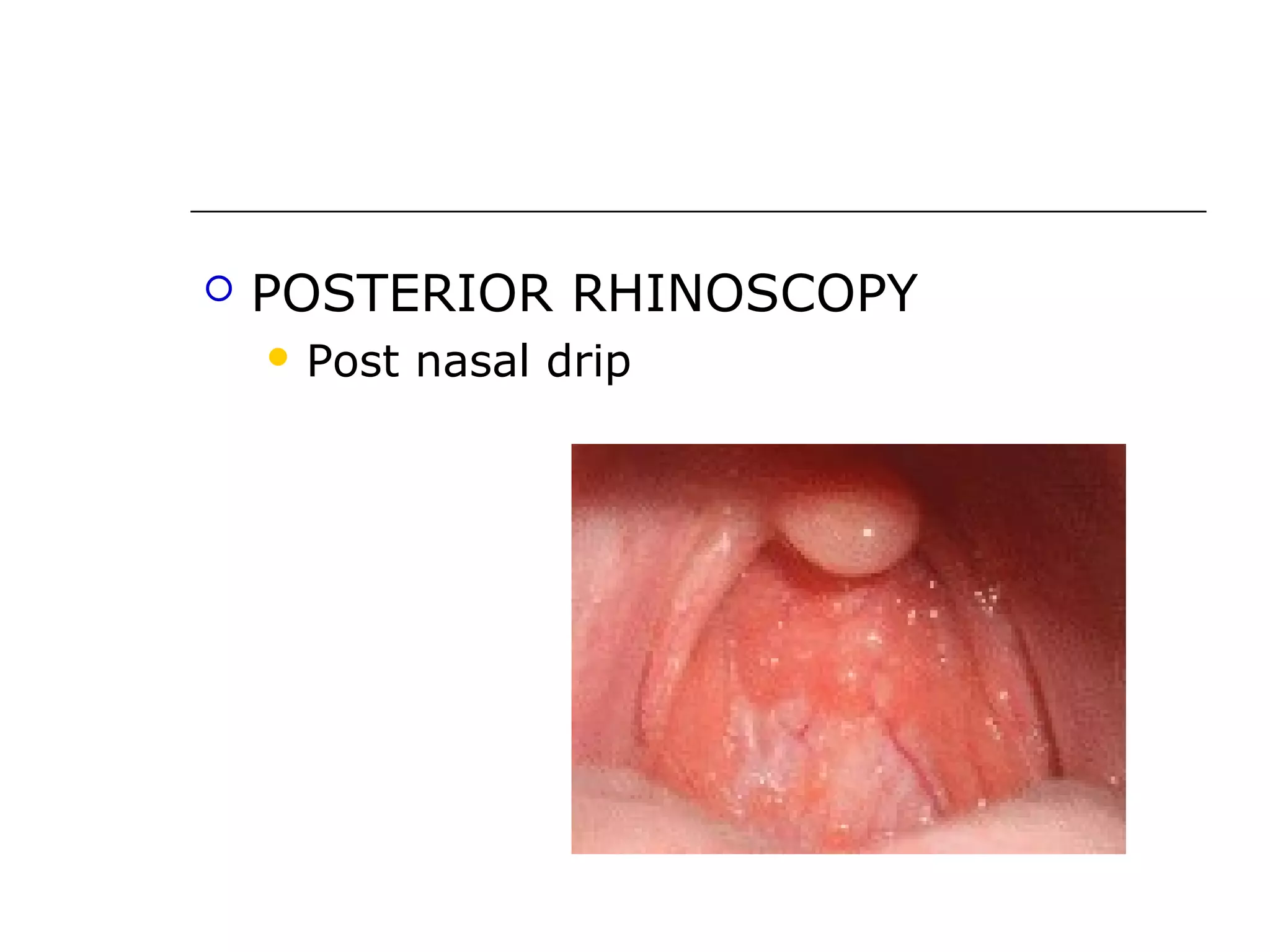
Vasomotor rhinitis is a chronic non-allergic rhinitis caused by an imbalance of the autonomic nervous system leading to hyperactivity of the nasal mucosa. Symptoms include recurrent sneezing, rhinorrhea, and nasal obstruction. The exact cause is unknown but it involves overactivity of the parasympathetic nervous system causing vasodilation and secretion from the nasal glands. Treatment focuses on avoiding triggers, using oral or topical decongestants and steroids, and in severe cases, short term systemic steroids or surgical procedures like turbinate reduction.