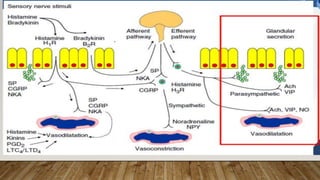
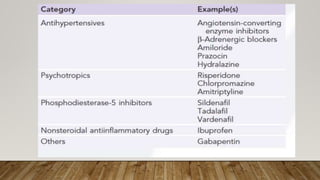
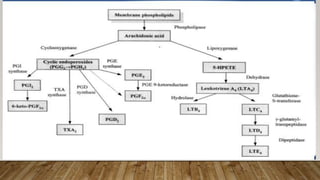
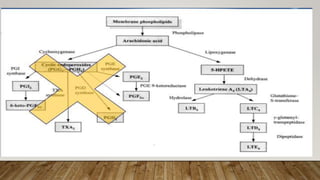
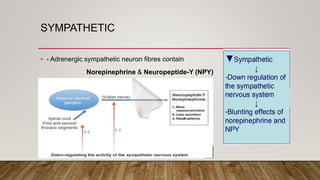
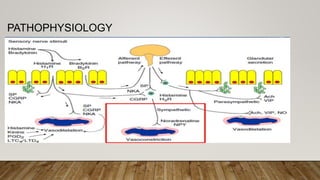
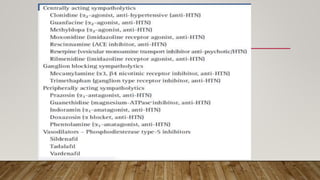
This document provides information about non-allergic rhinitis (NAR), including its various types and causes. It discusses vasomotor rhinitis as the most common form of NAR, accounting for at least 2/3 of cases. Other types include occupational rhinitis, hormonal rhinitis, food-induced rhinitis, and drug-induced rhinitis. It also describes NARES (non-allergic rhinitis with eosinophilia syndrome) which is characterized by nasal eosinophilia without evidence of allergy. The pathophysiology of NAR involves neurogenic mechanisms mediated by sensory C fibers and the autonomic nervous system leading to nasal inflammation and symptoms.