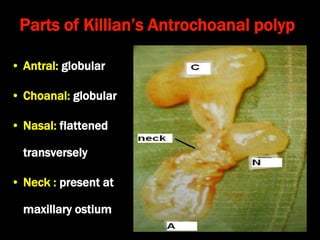
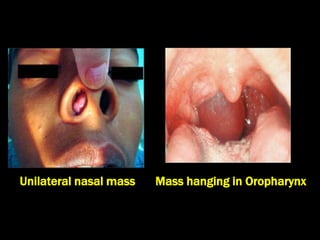
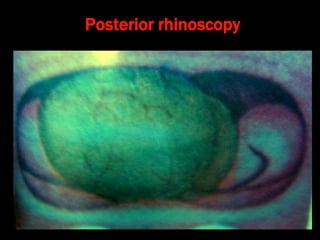
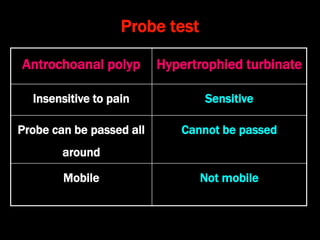
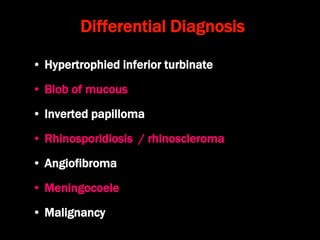
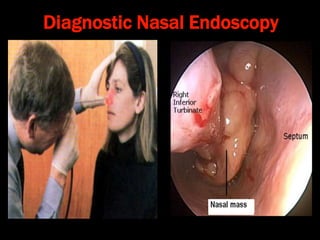
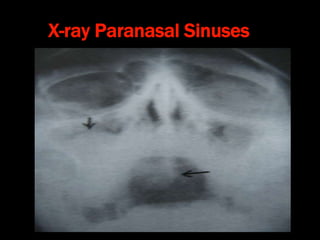
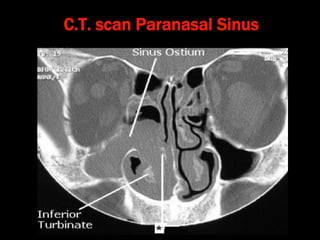
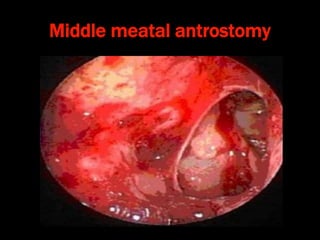
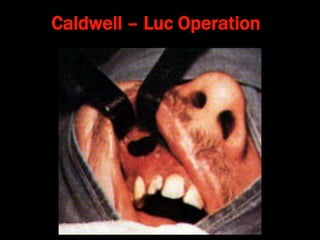
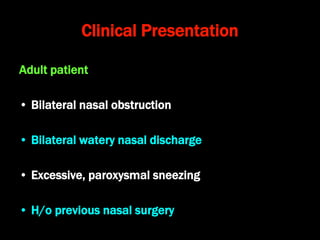
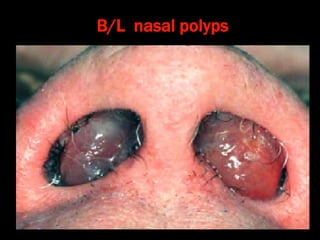
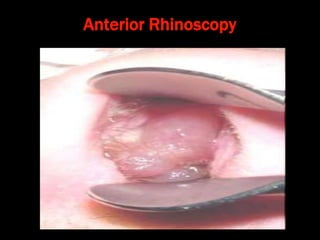
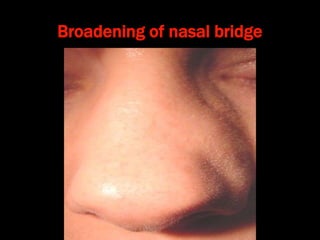
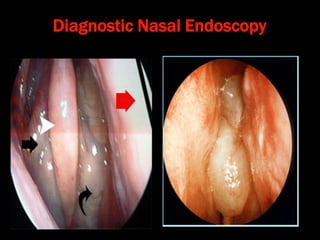
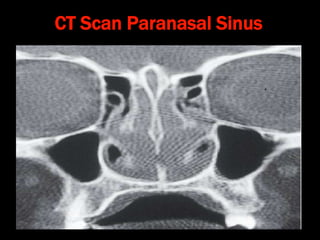
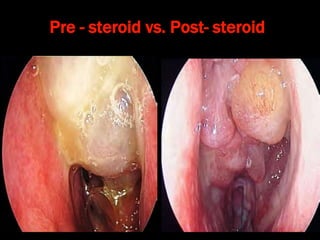
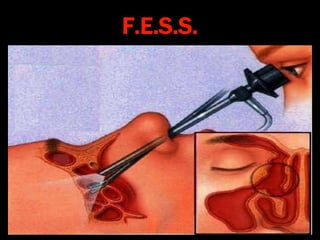
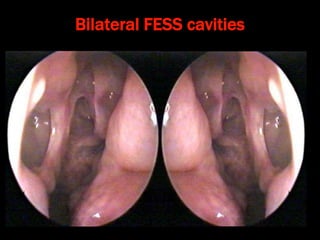
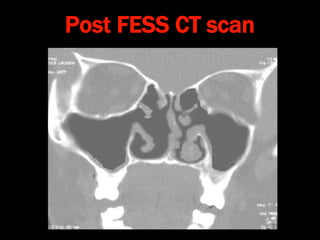
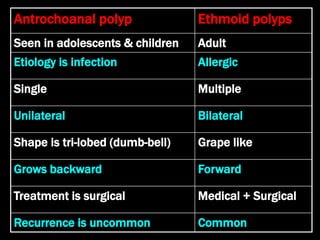
Nasal polyps can be either antrochoanal polyps, typically seen in children, or ethmoid polyps, more common in adults. Antrochoanal polyps originate in the maxillary sinus and extend backwards towards the nasopharynx, while ethmoid polyps originate in the ethmoid sinuses and grow forwards, often bilaterally. Treatment involves surgical removal of antrochoanal polyps and may require postoperative antibiotics to prevent recurrence, whereas ethmoid polyps are usually first treated medically with steroids and antihistamines and only require surgery if medical treatment fails or for large polyps.