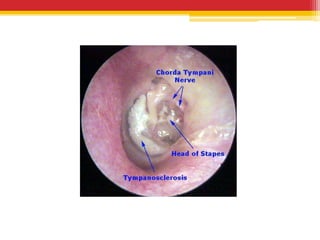
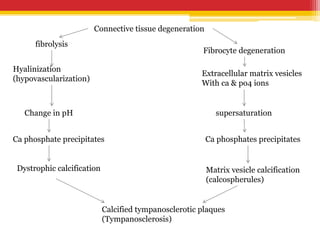
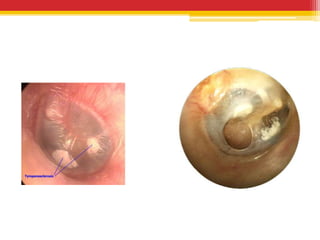
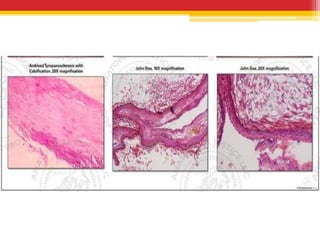
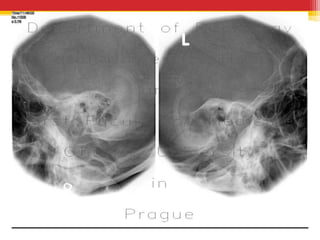
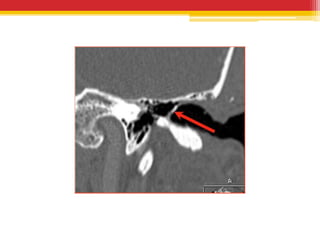
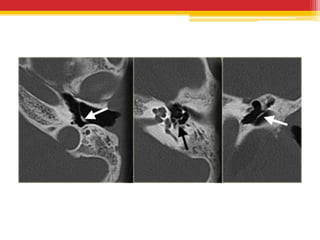
Tympanosclerosis is characterized by hyaline deposits in the tympanic membrane and middle ear space caused by chronic infection or inflammation. It results in the degeneration of connective tissue and deposition of calcium and phosphate. Common symptoms include conductive hearing loss and occasional tinnitus. Diagnosis is made by otoscopy showing white plaques and audiometry showing a conductive hearing loss. Treatment depends on the size and location of plaques, with small plaques sometimes removed before grafting but large plaques usually just addressed with hearing aids.