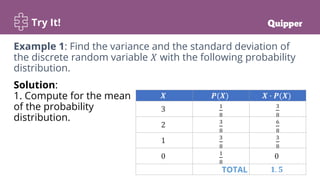
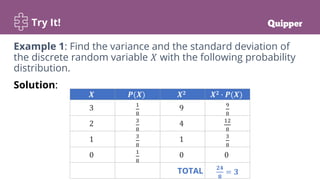
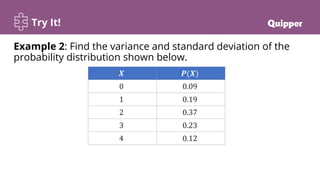
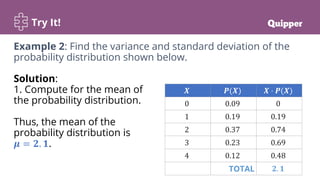
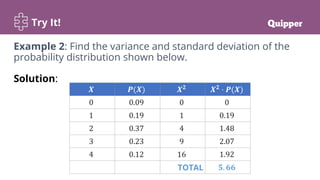
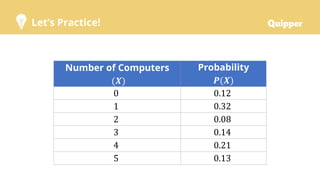
This document provides a lesson on calculating and interpreting the variance of a discrete random variable. It begins with objectives and essential questions. It then reviews standard deviation with an instructional video. Examples are provided to demonstrate how to calculate variance and standard deviation from a probability distribution by finding the mean, constructing columns for values squared and multiplied by probabilities, and using the variance and standard deviation formulas. Practice problems are given for individuals and groups. Key points define variance and standard deviation of a discrete random variable and properties of variance. Synthesis questions ask about determining variance and standard deviation from a distribution, measuring dispersion's importance, and constructing distributions for continuous variables.