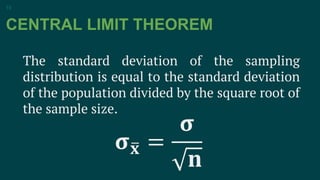
The central limit theorem states that as the sample size increases, the sampling distribution of the sample mean approximates a normal distribution, even if the population is not normally distributed. It defines the sampling distribution of the sample mean using this theorem. The document provides examples to illustrate how to calculate the mean and standard deviation of the sampling distribution based on the central limit theorem. It also shows how to use the z-score formula to solve probability problems involving the sampling distribution of the mean.