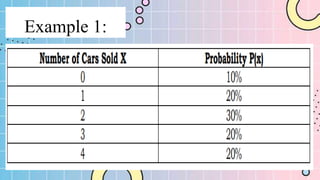
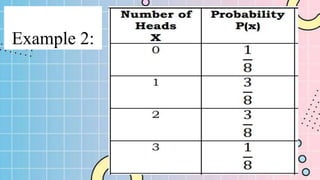
The document discusses the mean, variance, and standard deviation of discrete random variables. It defines the mean as the average value of the probability mass function and gives the formula to calculate it as the sum of each outcome multiplied by its probability. Variance is defined as the measure of how spread out the values are from the mean and is calculated using the given formula. Standard deviation is the square root of the variance and also measures the spread of the data from the mean. Examples are provided to demonstrate calculating the mean, variance, and standard deviation of probability distributions.